■ 3.1 Interface
The priority is higher on the main CPU interface, so the processing speed of the sound CPU depends on the operation of the main CPU.
The sound CPU program resides in sound memory. Therefore, all CPU programs are located in the address space of the sound CPU.
Figure 3.1 Access overview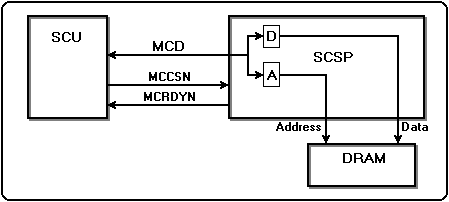
- Read and write in 16-bit units (word units).
→ 8-bit units (byte units) cannot be accessed from the main CPU. - When there is a read / write request, the address and data are fetched into the buffer in SCSP. As a result, "1" is output to the ready signal (MCRDYN) to the main CPU and a wait is generated. This wait continues until the processing inside the LSI is completed, so do not use continuous writing, which causes frequent occurrence of weights, except when the power is turned on.
- When the power is turned on, the time required to initialize the sound memory by continuous writing is approximately 100 msec with 4 Mbit DRAM.
■ 3.2 Memory access control
- PCM data read by PCM sound source, access by DSP
- DRAM refresh cycle
- DMA transfer
- Access by main CPU
- Access by sound CPU
Figure 3.2 Memory access priority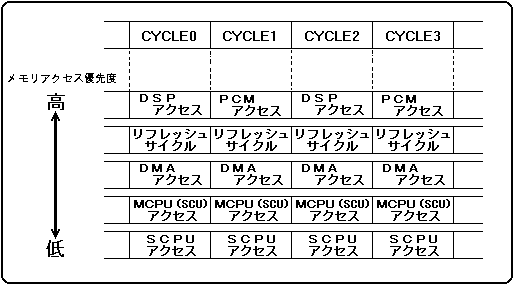
The memory cycle is performed 128 times between 1 sample (1 / 44.1K ≒ 22.68 μsec), and these 128 times are distributed to each device. Since the number of CPU accesses varies depending on the application, there is no best way to access memory, but please note the following points.
- Since the sound memory uses DRAM, a refresh cycle is required. The Saturn sound system requires two free cycles per sample, so other devices can use 126 memory cycles.
- The sound source and DSP memory cycles have the highest priority memory cycle.
- Since the sound source uses two memory cycles per slot sound, a total of 64 memory cycles are used for a maximum of 32 slots.
When the EG is in the maximum attenuation state ("3FFH"), the sound source does not access the memory. Set KEY_OFF for slots that do not output audio. - The DSP makes up to 64 memory accesses. This depends on the DSP application. If you want to temporarily store data in the DSP, use the registers inside the DSP as much as possible.
- If you are using DMA with built-in SCSP, the sound CPU will have a considerable weight, which will slow down the sound CPU.
 ★ HARDWARE Manual ★ SCSP User's Manual
★ HARDWARE Manual ★ SCSP User's Manual