◆ Execution of JUMP instruction
Figure 4.2 Execution of JUMP instruction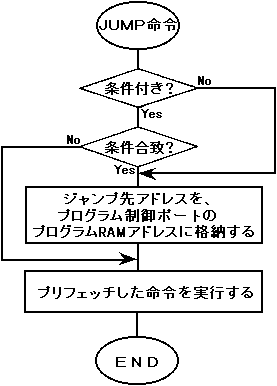
◆ Execution of LOOP program
Figure 4.3 Executing the LOOP program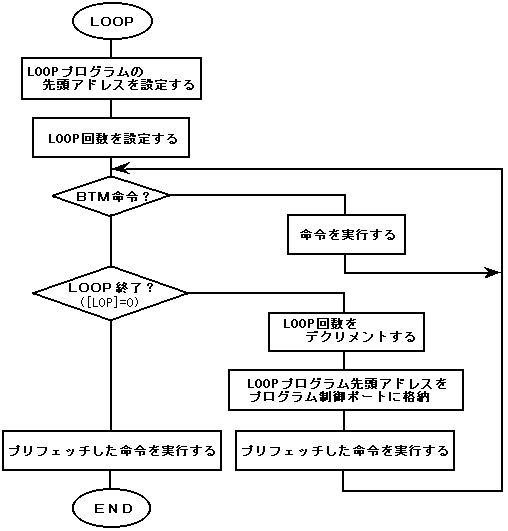
◆ Execution of DMA instruction
- Data transfer from D0 bus to DSP
- Data transfer from DSP to D0 bus
● Data transfer from D0 bus to DSP
See Section 4.5, " Instruction Details " for more information.
MOV SImm, [CT0]; DSP data RAM0 transfer start address set MVI Imm, [RA0]; external memory transfer start address set DMA D0, [MD0], SImm; DMA transfer start using D0 bus
Item | feature |
Set of flags | The TO flag of the program control port is set. |
Start and end | Follows an external data ready signal. By this signal, it is transferred in units of one longword. In addition, the DMA transfer is terminated by the end signal from the outside, and the TO flag of the program control port is reset at this timing. |
Address update | For each longword transfer, the DSP data RAM transfer address ([CTO-3]) is added by 1, and the external memory transfer address ([RA0]) is added according to the number of added addresses. |
Hold state | When the Hold bit of the DMA instruction (see Section 4.5, "Instructions", DMA Instructions) is set to 1, |
● Data transfer from DSP to D0 bus
MOV SImm, [CT0]; DSP data RAM0 transfer start address set MVI Imm, [WA0]; external memory transfer start address set DMA [MD0], D0, SImm; DMA transfer start using D0 bus
Item | feature |
Set of flags | The TO flag of the program control port is set. |
Start and end | Follows an external data ready signal. By this signal, it is transferred in units of one longword. In addition, the DMA transfer is terminated by the end signal from the outside, and the TO flag of the program control port is reset at this timing. |
Address update | For each longword transfer, the DSP data RAM transfer address ([CTO-3]) is added by 1, and the external memory transfer address ([WAO]) is added according to the number of added addresses. |
Hold state | When the Hold bit of the DMA instruction (see Section 4.5, "Instructions", DMA Instructions) is set to 1, |
 ★ HARDWARE Manual ★ SCU User's Manual
★ HARDWARE Manual ★ SCU User's Manual