3.1 Processing flow
The main processing flow is shown in Figure 3.1.
Figure 3.1 Processing flow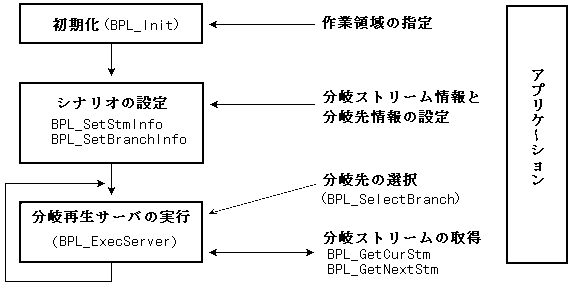
3.2 Scenario
The branch stream is specified for each file. Data such as audio and video can be retrieved by channel interleaving within the file.
Figure 3.2 Stream branching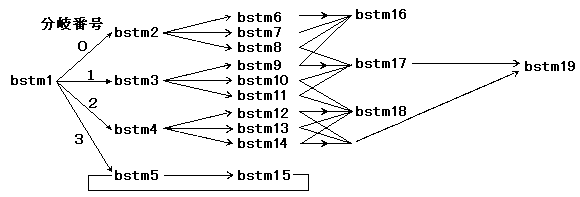
- In this scenario, the first branch stream to read is bstm1. The branch playback library starts loading bstm1.
- The application gets the currently loading branch stream and sets it in the decoder.
- The branch playback library starts reading bstm1, followed by branch candidates (branch streams that may be retrieved next), bstm2, bstm3, bstm4, and bstm5. By pre-reading the stream of branch candidates in this way, the CD buffer can be used effectively and smooth branching is possible.
- The application gets the event from the pad input etc. and selects the branch destination. If a branch number from 0 to 3 is assigned to the branch to bstm2, bstm3, bstm4, and bstm5 and 1 is specified, reading of bstm2, bstm4, and bstm5 that are no longer needed will be stopped. If necessary, the application gets the stream to branch to and sets it in the decoder.
- When the extraction of bstm1 is completed, the extraction of bstm3 will start. When the application specifies branch execution to the branch playback server, the branch playback library starts reading bstm9, bstm10, and bstm11 as in (c).
[Notes] The same stream must not exist in one branch candidate. This is because opening the same stream with a different stream handle does not read the data at the same time. A stream that is opened later is connected to the end of the aperture, so data can be retrieved from the stream that was opened earlier. Therefore, the same stream as it is now can exist in the branch candidates. << Example in Figure 3.2 >> -The same stream must not be duplicated in bstm6-8, You can have the same stream as bstm2.
3.3 State transition of branch playback
Status | explanation |
|---|---|
Branch playback end | Branch playback is complete. |
Waiting for branch destination selection | The branch candidate is pre-read, but the branch destination is not selected. |
Branch destination decision | A branch destination has been selected from the branch candidates. |
No branch destination | There are no branch candidates or branch destinations for the current stream. |
Figure 3.3 State transition diagram of branch playback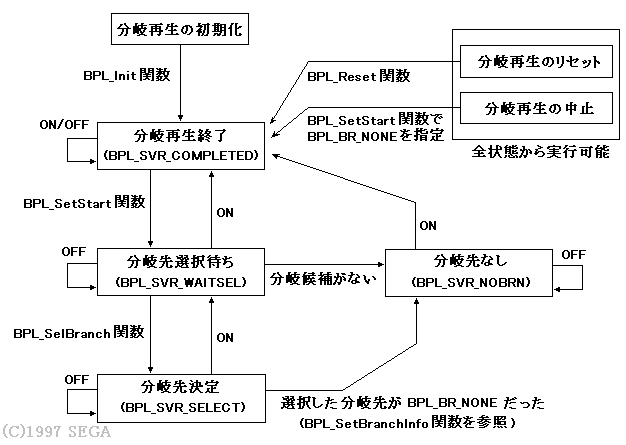
If ON is specified in the branch destination determination state, the branch stream is switched.
3.4 Branch execution (branch stream switching process)
- Closes the current stream A.
(Stops reading A and erases any data left in the CD buffer.) - The branch destination stream B becomes the new current stream.
- The branch destination stream is undecided.
Branch stream | Before branch execution | After branch execution (after switching process) |
|---|---|---|
Current stream (obtained by BPL_GetCurStm function) | A | B |
Branch destination stream (obtained by BPL_GetNextStm function) | B | Undecided until the next branch destination is selected (select / determine with BPL_SelectBranch function) |
- The playback start stream specified by the BPL_SetStart function is first opened as the current stream.
- When the current stream starts loading, the branch candidate stream is opened.
- When you select a branch destination, other branch candidates are closed and only the branch destination is read ahead.
- When you perform a branch, its current stream is closed.
The branch destination stream switches to the current stream and repeats (b) to (d). - When the branch playback ends, the stream group is closed.
timing | explanation |
|---|---|
Natural switching | After decoding stream A, switch to stream B at the branch destination. |
Forced switching | Even during the decoding of stream A, it is forcibly switched to stream B of the branch destination. |
For either natural or forced switching, execute the switching process for the decoder first, and then turn on the branch execution switch after that is completed.
 ★ PROGRAMMER'S GUIDE ★ Branch playback library
★ PROGRAMMER'S GUIDE ★ Branch playback library