3.1 Initialization
- Library work area initialization
- Mount process
The size of the area changes depending on the number of files opened at the same time, so find it with the following macro. Where open_max is the maximum number of files that can be opened at the same time.
Initialize the directory information management structure and call GFS_Init as follows.
#define OPEN_MAX 20 / * Maximum number of files to open at the same time * / #define MAX_DIR 10 / * Maximum number of directory information * /Uint32 work [GFS_WORK_SIZE (OPEN_MAX) / 4]; / * Library work area * / GfsDirTbl dirtbl; / * Directory information management structure * / GfsDirId dir [MAX_DIR]; / * Directory information storage area * /
GFS_DIRTBL_TYPE (& dirtbl) = GFS_DIR_ID; / * Directory information storage area type * / GFS_DIRTBL_NDIR (& dirtbl) = MAX_DIR; / * * / in the directory information storage area / * Maximum number of elements * / GFS_DIRTBL_DIRID (& dirtbl) = dir; / * Directory information storage area * / / * Address * / GFS_Init (OPEN_MAX, work, & dirtbl);
3.2 File identifier
When accessing by file name, convert the file name to a file identifier.
The file identifier is valid for the current directory.
Figure 3.1 Access by file identifier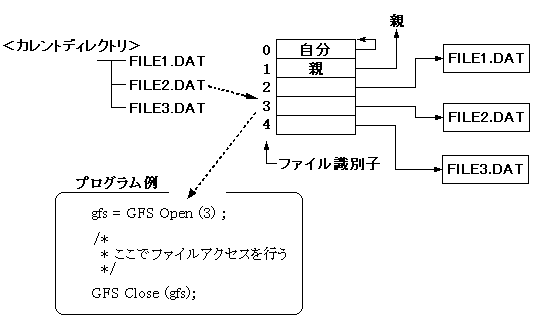
3.3 Subdirectory operations
- Load directory information (GFS_LoadDir)
- Current directory setting (GFS_SetDir)
At this time, the following two types can be selected as the directory information retention area.
- Does not retain the file name. Only access by file identifier is possible.
- Since it holds the file name, it requires a larger area than (a).
- It can be accessed by file name.
Figure 3.2 Setting directory information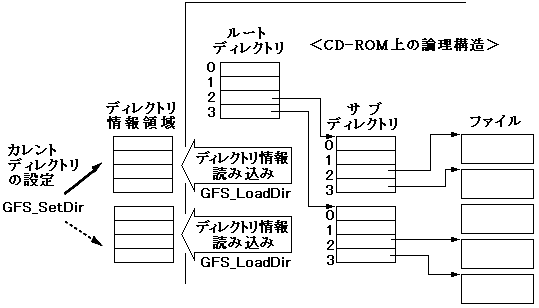
Current directory setting ↓
Open file ↓
Access to files ↓
File close
#define MAX_DIR 10 / * Maximum number of directory information * / GfsDirTbl dirtbl; / * Directory information storage area * / GfsDirId dirid [MAX_DIR]; / * Directory information storage area * / Sint32 dir_fid; / * Contains directory file identifier * / Sint32 fid; / * Contains the identifier of the file to access * / GfsHn gfs; / * File handle of the file to access * / GFS_DIRTBL_TYPE (& dirtbl) = GFS_DIR_ID; GFS_DIRTBL_NDIR (& dirtbl) = MAX_DIR; GFS_DIRTBL_DIRID (& dirtbl) = dirid; GFS_LoadDir (dir_fid, & dirtbl); / * Load directory information * / GFS_SetDir (& dirtbl); / * Current directory setting * / / * Set the identifier of the file that accesses fid * / gfs = GFS_Open (fid); / * * Access files here * / GFS_Close (gfs);
The following is an example of accessing two files in two subdirectories directly under the current directory at the same time. Suppose the file identifiers of the two subdirectories containing the files you want to access are specified by dir_fid1 and dir_fid2, respectively.
#define MAX_DIR1 10 / * Maximum number of directory information in dir_fid1 * / # define MAX_DIR2 10 / * Maximum number of directory information in dir_fid2 * / GfsDirTbl curdir; / * Current directory at this point * / GfsDirTbl dirtbl1, dirtbl2; / * Directory information management area * / GfsDirId dirid1 [MAX_DIR1]; / * Directory information storage area * / GfsDirId dirid2 [MAX_DIR2]; / * Directory information storage area * / Sint32 dir_fid1, dir_fid2; / * Contains the directory file identifier * / Sint32 fid1, fid2; / * Contains the identifier of the file to be accessed * / GfsHn gfs1, gfs2; / * File handle of the file to access * / / * Read the directory information of dir_fid1 in the current directory * / GFS_DIRTBL_TYPE (& dirtbl1) = GFS_DIR_ID; GFS_DIRTBL_NDIR (& dirtbl1) = MAX_DIR; GFS_DIRTBL_DIRID (& dirtbl1) = dirid1; GFS_LoadDir (dir_fid1, & dirtbl1); / * Read the directory information of dir_fid2 in the current directory * / GFS_DIRTBL_TYPE (& dirtbl2) = GFS_DIR_ID; GFS_DIRTBL_NDIR (& dirtbl2) = MAX_DIR; GFS_DIRTBL_DIRID (& dirtbl2) = dirid2; GFS_LoadDir (dir_fid2, & dirtbl2); / * Open fid1, a file in directory dir_fid1 * / GFS_SetDir (& dirtbl1); gfs1 = GFS_Open (fid1); / * Open fid2, a file in directory dir_fid2 * / GFS_SetDir (& dirtbl2); gfs2 = GFS_Open (fid2); / * * Access files here * / GFS_Close (gfs1); GFS_Close (gfs2);
3.4 Mutual conversion of file name and file identifier
Calling these functions while setting directory information that does not include a file name to the current directory will result in an error.
An example of defining a function that opens a file with a file name using this function is shown below.
[Example] / * Open the file specified by the file name * /
GfsHn OpenByName (Sint8 * fname)
{
Sint32 fid = GFS_NameToId (fname);
if (fid <0) {
return NULL;
}
return GFS_Open (fid);
}
3.5 CD block file system
The process for initializing, reading directory information, and setting the current directory using CDBFS is shown below.
Table 3.1 shows the advantages and disadvantages of using CDBFS.
Strong Points | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
-The host memory usage is low. | -The CD-ROM is accessed every time a file in a different directory is accessed. |
-The CD buffer that can be used by the application is reduced by one partition. | |
-The file name cannot be used. |
Using a file name while setting the current directory of CDBFS will result in an error.
 ★ PROGRAMMER'S GUIDE ★ File system library
★ PROGRAMMER'S GUIDE ★ File system library