1.1 Purpose
These routines fall into the following categories:
The viewpoint position is the origin, and the screen position is -1.0 on the Z axis.
(1) Supports 2D and 3D coordinates
(2) Tangent vector at each output coordinate can be acquired As shown in Fig. 1, it is possible to acquire a point on a curve that smoothly passes through that point by specifying a small number of points. Figure 1 shows that if you specify the input coordinate array P0 to 3, the number of arrays 4, and the number of output coordinates 10, you can obtain an array of output coordinates that smoothly passes through that point as c0 to 9. You can also get the tangent vector at each output coordinate by using the tangent function. The tangent vector can be used for the direction of travel of the character.
Figure 1 Conceptual diagram of curve calculation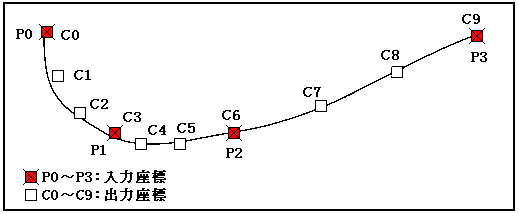
 ★ PROGRAMMER'S GUIDE ★ Mathematical calculation library
★ PROGRAMMER'S GUIDE ★ Mathematical calculation library