
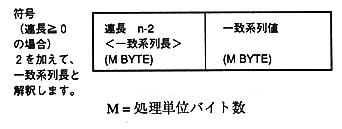
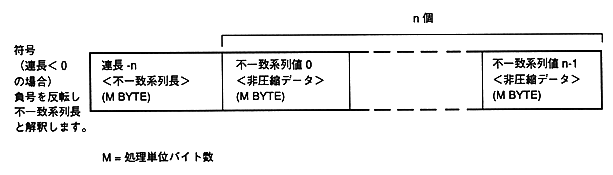
Figure 1.3 Run-length compressed file format
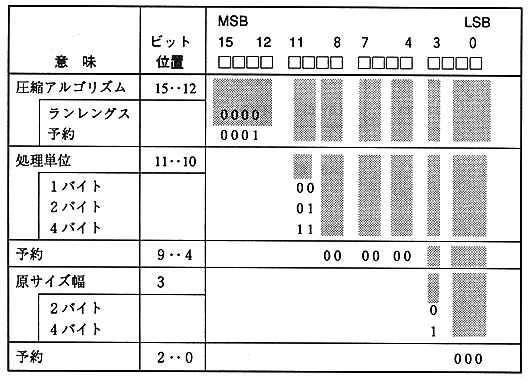
1.3 Decompression library
[Overview]
You can store the compressed data on a CD-ROM as a separate file or have it in any other way. However, when decompressing, the decompression library is started by specifying the input data buffer and the output data buffer in the memory that can be accessed directly from the main CPU.
Both of these buffers must be allocated by the user of the decompression library and their address specified in the library function.
For example, when reading the input data from the CD and decompressing it, it is necessary to read the input data of one decompression process into the memory to the end and then start the decompression library function.
The user also informs the decompression library function of the output data buffer size. If the decompressed data exceeds this size, the library function does not write to the position that exceeds the size and interrupts the process. You can also use this function to intentionally perform halfway decompression processing.
However, there is no function to resume the interrupted decompression process.
The following figure gives an overview of the decompression process.
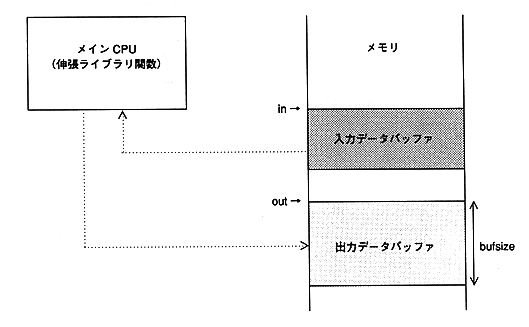
in: Input buffer start address. Align with 4-byte boundaries. out: Output buffer start address. Align with 4-byte boundaries. bufsize: Output buffer size. An integer multiple of the number of processing unit bytes.
[Module configuration]
If you want to link only the bare minimum of object code, you can use lower level functions. In this case, you need to be careful not to make a difference with the operation on the compression tool side.
The following figure shows the module structure of the decompression library.
Figure 1.5 Module configuration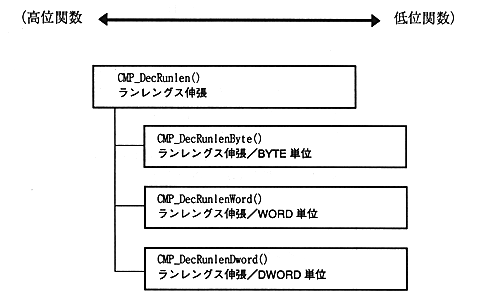
[Example of use]
When invoking a function, it is assumed that the compressed data is in memory that can be accessed directly from the main CPU.
#include "cmplib.h"
/ * Compressed by the compressed data run length method,
Convert to compressed file data with binary text converter * /
char comdata [] = {
0x10, 0x01, 0x04, ・ ・ ・ ・ ・ ・ ・ ・
::
::
::
}
/ * Decompressed data buffer (make sure that the size is not smaller than the size before compression.) * /
char outputbuf [4096];
::
::
::
−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−–
main ()
{
/ * Decompressed data pointer * /
char * buf;
/ * Set at the beginning of the decompressed data buffer * /
bufp = outputbuf;
/ * Run-length dictionary extension * /
CMP_DecRunlen (cmpdata, & bufp, sizeof (outputbuf));
/ * Use of decompression data * /
::
::
::
}
#include "sega_gfs.h"
#include "cmplib.h"
/ * File read buffer * /
Uint8 readbuf [READ_SIZE]
/ * Decompressed data buffer * /
Uint8 outputbuf [4096]
−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−–
main ()
{
GfsFid fid; / * File size identifier * /
Sint32 fsize; / * File size * /
char * bufp;
fid = 5; / * Specify compressed data file identifier * /
/ * Bulk reading of files * /
fsize = GFS_Load (fid, 0, readbuf, READBUF_SIZE);
/ * Set at the beginning of the decompressed data buffer * /
bufp = outputbuf;
/ * Run-length extension * /
CMP_DecRanlen (readbuf, & bufp, sizeof (outoutbuf));
/ * Use of decompression data * /
::
::
::
}
 ★ PROGRAMMER'S GUIDE ★ Compression / decompression library
★ PROGRAMMER'S GUIDE ★ Compression / decompression library