● Read / write access by CPU
VRAM access by the CPU can only be specified in units of access to VRAM-A or access to VRAM-B, not in units of banks.
To specify VRAM access by the CPU for VRAM that is not divided into two, specify the CPU read / write access command in the VRAM cycle pattern register at the timing of access. At this time, it is the same even if you specify an access command that does not access instead of the CPU read / write access command. Also, when the access command for the screen (pattern name data read, character pattern data read, or bitmap pattern data read) that is set not to be displayed is set in the screen display enable register, CPU read / write access is set. Become. For details on the screen display enable register, see " 4.1 Screen Display Control."
If you specify a CPU read / write or no access command for all access timings of VRAM that is not divided into two, CPU access is possible at any time during the screen display period. You can use this to use one of the VRAMs as auxiliary work RAM. Also, by switching the VRAM used to display the picture like a frame buffer, you can display the picture while rewriting it at high speed.
For example, if VRAM-A is not divided into two banks, the VRAM cycle pattern register specification for CPU read / write access to T2 and T4 is shown in Figure 3.6.
Figure 3.6 Example of CPU read / write access specification when VRAM is not divided into 2 banks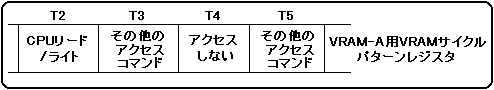
Figure 3.7 Example of CPU read / write access specification when dividing VRAM into 2 banks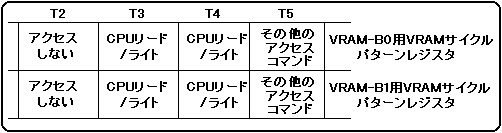
 ★ HARDWARE Manual ★ VDP2 User's Manual ★ Chapter 3 RAM
★ HARDWARE Manual ★ VDP2 User's Manual ★ Chapter 3 RAM