2.1 Terminology
the term | meaning |
|---|---|
MPEG buffer | Memory area managed by MPEG / Video LSI. |
Frame buffer | Area where the decoded image data is stored. It consists of multiple frame banks. It consists of 4 banks for normal resolution and 1 bank for high-definition resolution. |
Frame bank | The area where the image data for one picture of the MPEG video stream is expanded. |
VBV buffer | Area used to decode an MPEG video stream. It is allocated in the MPEG buffer. |
Display window | A rectangular area on the TV monitor where the MPEG video is output. |
Framebuffer window | A rectangular area set for the framebuffer. |
Bright spot | The smallest display unit on the display. |
Pixel | A display unit consisting of 2x2 bright spots at normal resolution and 1x1 bright spots at high-definition resolution. |
Image data | Decoded color data. 16 to the host area |
MPEG window | An object for controlling the display window and framebuffer window. |
MPEG video handle | An object for controlling MPEG video. |
MPEG still image handle | An object for controlling MPEG still images. |
MPEG handle | A generic term for MPEG video handles and MPEG still image handles. |
MPEG report | Data that represents the state of the MPEG system. |
2.2 MPEG stream
Picture type | explanation |
|---|---|
I picture (Intra-coded Picture) | An image that can be decrypted only from your own information. Although the compression efficiency is poor, random access is possible if this image is inserted at regular intervals. |
P picture (Predictive-coded Picture) | An image that uses another already decoded picture (I, P) as the predicted image. |
B picture (Bidirectionally) | An image that uses two pictures (I, P) before and after as a prediction image. The compression efficiency is the best. |
Figure 2.1 Predictive relationship between pictures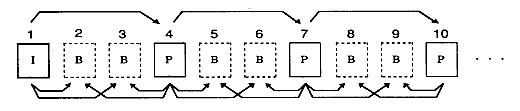
In order to decode the B picture, the I picture or P picture that is the predicted image must be decoded first. Therefore, the order in which the pictures are input to the decoder and the actual display order are interchanged.
Figure 2.2 Order on CD-ROM and playback image order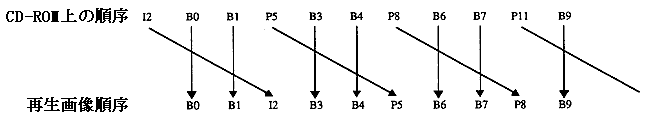
 ★ PROGRAMMER'S GUIDE ★ MPEG library
★ PROGRAMMER'S GUIDE ★ MPEG library