- The MPEG library has two modes of operation for playing video:
- (1) Video playback mode
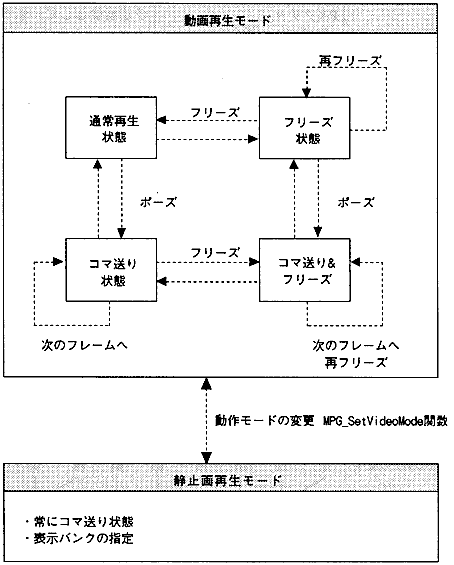
- This is the mode to play the video. There are normal playback state, freeze state, pause state, and pause & freeze state.
- (2) Still image playback mode
- This mode is for playing back still images. Images for 4 banks at normal resolution and 1 bank at high resolution can be displayed.
Audio can always be played. You can also synchronize video and audio. Figure 3.1 Operation mode
3.1 Video playback
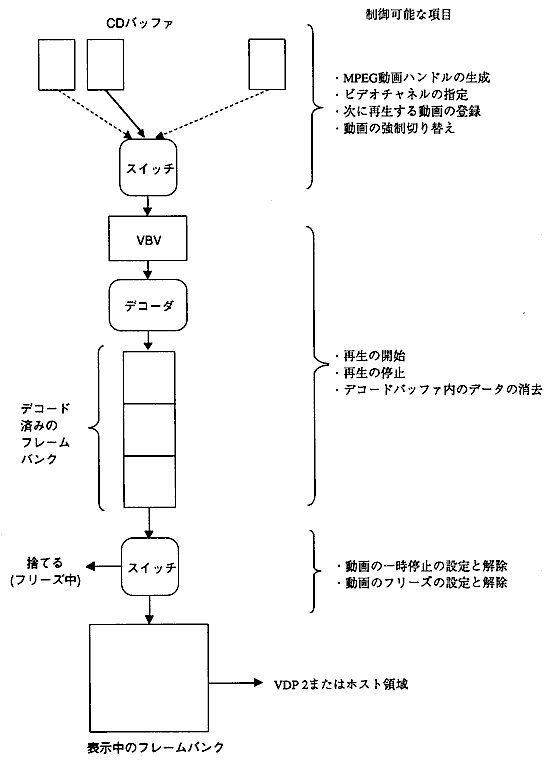
- The MPEG video data is read from the CD into the CD buffer and expanded by the decoder into the frame bank. The image data expanded in this frame bank is displayed in sequence to create a movie. There are two ways to display the frame bank data, one is to output directly to VDP2 and the other is to transfer it to VRAM by the host and display it. The data flow is shown below.
Figure 3.2 Data flow during video playback
3.2 Still image playback
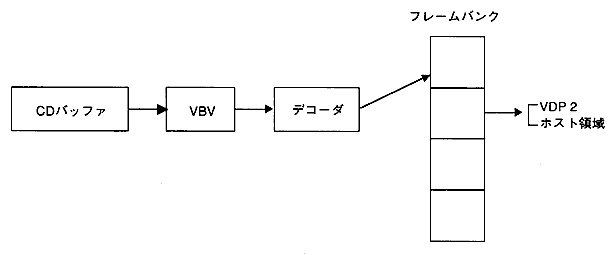
- In still image playback mode, the video stream data in the CD buffer can be decoded by specifying the frame bank number. You can specify the frame bank number to output and output it directly to VDP2, or transfer it to VRAM by the host and display it.
Figure 3.3 Data flow during still image playback
3.3 Image data output method
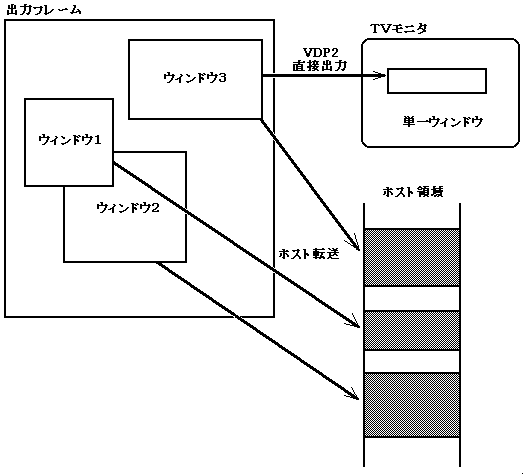
- You can create an output window in the image data area in the output frame bank and output the data. There are the following two methods for outputting data.
- VDP2 direct output method
- Host forwarding method
- You can create multiple output windows when transferring to the host area and only one output window when outputting directly to VDP2.
You can also add various visual effects to these windows. Figure 3.4 Output window
- Video effect
- Cropping (cutting out the image)
- Enlargement / reduction
- fade
- Mosaic / blur
- Luminescence key
3.4 Playback of MPEG audio
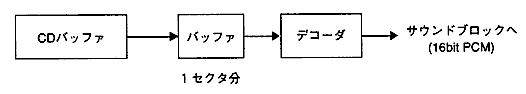
- Playback of MPEG audio is performed by decoding the stream data read from the CD buffer and outputting it to the sound block.
Figure 3.5 Audio playback





 ★ PROGRAMMER'S GUIDE ★ MPEG library
★ PROGRAMMER'S GUIDE ★ MPEG library