4.1 MPEG / Video Decoder- The structure of the MPEG / Video decoder is shown in Figure 4.1.
- Figure 4.1 Structure of MPEG / Video Decoder
Controllable items 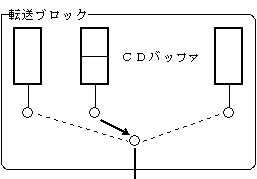
《Transfer block》
・ Registration of stream to be played ・ Registration of stream to be played next ・ Transfer of stream data ・ Forced switching of video 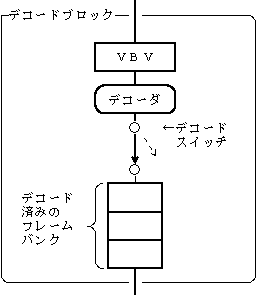
《Decode block》
-Start decoding-Stop decoding-Clear data in the decoder buffer 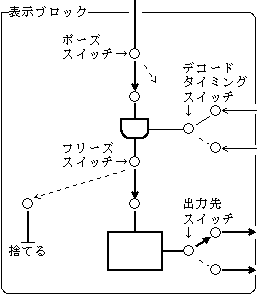
《Display block》
・ Switching decoding timing ・ Setting and canceling video pauses ・ Setting and canceling video freezes ・ Switching output destinations
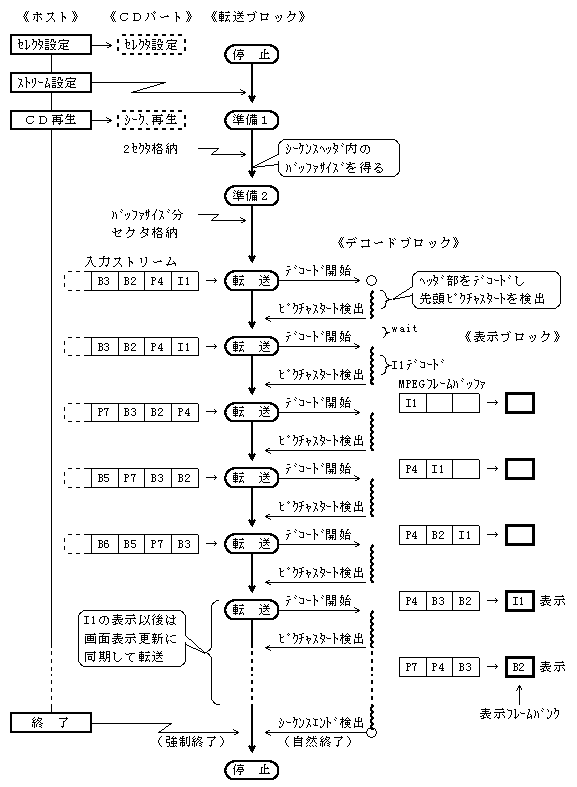
- 4.1.1 Overview of MPEG / Video Decoder Operation
- Figure 4.2 shows an overview of the operation of the MPEG / Video decoder.
- Figure 4.2 Overview of MPEG / Video decoder operation
- 4.1.2 MPEG / Video Decode Block
- The decode block controls the start / stop of decoding and the erasure of the decoder buffer (VBV buffer and MPEG frame buffer).
- (1) Start / stop decoding
- You can directly control the decode switch of the MPEG / Video decoder.
If the decoding is instructed to stop while decoding a certain video stream, the decoding of the picture being processed is completed, and the decoding is stopped when the decoder detects the next picture start code.- Stream A decoding
VBV buffer MPEG frame buffer ┌────┬─┬──┐ ┌────┐ ┌─┬──┬───┬───┐
│ │ | │ → │ Decoder │ → │ | │ │ │ │
└────┴─┴──┘└────┘└─┴──┴───┴───┘
Undecoded ↑↑
│ Decoded │
Start next picture
- Decoding stop instruction
VBV buffer MPEG frame buffer ┌────┬────┐ ┌────┐ ┌─┬──┬───┬───┐
│ │ │ → │ Decoder │ → │ | │ │ │ │
└────┴────┘└────┘└─┴──┴───┴───┘
↑↑
Start next picture Decoding of the picture in process is complete
- (2) Stream switching and decoder buffer erasure
- When switching streams, the data of the previously decoded stream remains in the following decoder buffer. This data needs to be erased.
- VBV buffer
- The undecoded part of the picture currently being processed and the pre-read data after that remain.
- MPEG frame buffer
- The decoded part of the picture currently being processed and the picture data that has already been decoded remain.
- (3) Clearing the VBV buffer
- Wait for the picture start code to clear the VBV buffer and switch to another stream.
Following the decoded picture in the MPEG frame buffer, the pictures in the subsequent stream can be played smoothly.
If the VBV buffer is erased immediately without waiting for the picture start code, the picture in the process of decoding in the MPEG frame buffer may not be able to complete the processing, resulting in a decoding error. - (4) Erasing the MPEG frame buffer
- If you just erase the VBV buffer and switch to another stream, the decoded pictures in the MPEG framebuffer will be displayed first. As a result, there is a delay of 3 frames in stream switching.
To avoid this delay, the decoded data in the MPEG frame buffer can be erased at the same time as the VBV buffer. - 4.1.3 MPEG / Video display block
- The display block controls the output of the image data decoded in the decoding block.
In the following description, repause is an operation in which the pause switch is open, waits for a certain decoding timing, closes the switch, and opens at the next decoding timing. The same applies to the refreeze and freeze switch. - (1) Display block function
- The display block has the following functions.
- Decoding timing switching Specifies the timing of the decoding synchronization signal. You can specify whether to decode by VSYNC synchronization or by host synchronization.
- Setting and releasing the pose of the video Set the pose of the video by opening the pause switch. During the pause, the image data does not flow beyond the pause switch, so the image is not updated. Unpause the video by closing the pause switch.
In addition, slow playback can be performed by specifying the repause interval. - Setting and releasing the video freeze Set the video freeze by opening the freeze switch. During the freeze, the image data is discarded from the freeze switch, so the image is not updated. Unfreeze the video by closing the freeze switch.
In addition, strobe playback can be performed by specifying the refreeze interval. - Switching the output destination Switch the output destination of the image data. VDP2 and host can be set as the output destination.
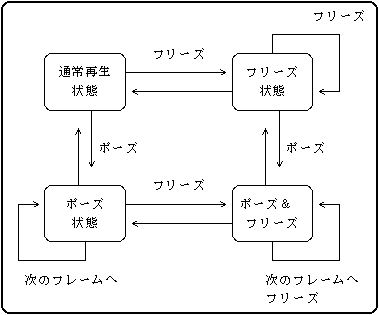
- (2) State transition of display block
- The display block has the following states.
- Table 4.1 Display block status
Status Switch status
explanation Pause Freeze 1 Normal playback
Closed Closed It is playing normally. 2 Pause
Open Closed The video is stopped.
The image data is stopped at the pause switch. 3 Freeze
Closed Open The video is stopped.
The image data is discarded from the freeze switch. Four Pause&
Freeze
Open Open The video is stopped.
The image data is stopped at the pause switch.
Even if the pause is released, it freezes and the video does not resume playing.
- Figure 4.3 shows the state transition diagram of the display block of the MPEG / Video decoder.
Figure 4.3 State transition diagram of MPEG / Video display block
4.2 MPEG / Audio Decoder
- The MPEG / Audio decoder takes a sector from the specified buffer partition and decodes it. The decoded data is sent to the sound block (SCSP) by a serial line.
The structure of the MPEG / Audio decoder is shown in Figure 4.4.- Figure 4.4 Structure of MPEG / Audio Decoder
Controllable items 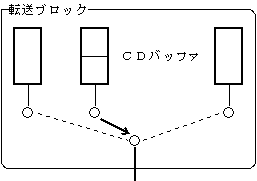
《Transfer block》
-Registration of the stream to be played-Registration of the stream to be played next-Transfer of stream data-Switching of streams-Setting of stream number and channel number 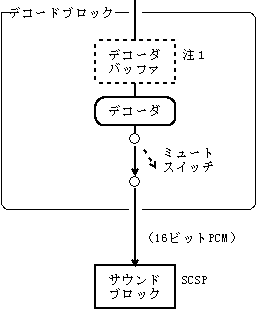
《Decode block》
-Start decoding-Stop decoding-Mute audio
- Note 1 : For the decoder buffer, the processing target sector area in the CD buffer partition is used.
- 4.2.1 MPEG / Audio decoding block function
- The audio decode block has the following functions.
- Start decoding / Stop decoding
- Audio mute
- Get audio timestamp
- (1) Audio mute
- The following settings can be made for the MPEG audio decoder.
- LR channel mute <BR> Mute left and right independently.
- Automatic mute at the start of stream input When a stream is input to the audio decoder, the data (about 100 msec) for the first three audio frames is muted.
- 4.2.2 Playback of multiple channels
- When playing in multiple languages (multilingual), MPEG audio data is assigned to each channel number.
When the channel to be played back is set, only the data of that channel is sent to the decoder. Since the data of other channels is discarded according to the transfer of the playback channel, the audio synchronized with the video can be played immediately even if the channel is switched to another channel.
Figure 4.5 shows an example of multilingual playback. Figure 4.5 Multilingual playback
Buffer partition ┌────┬────┬────┬────┬────┬────┬────┐ ┌────┐
│ CN = 3 │ CN = 2 │ CN = 1 │ CN = 3 │ CN = 2 │ CN = 1 │ CN = 3 │ CN = 1 │ Decoder │
│ France │ English │ Japanese │ French │ English │ Japanese │ French │ → │ │ │
└────┴────┴────┴────┴────┴────┴────┘└────┘
An example of playing Japanese with channel number 1 (CN = 1) is shown.
French and English audio data will be discarded as the Japanese data is played.
| Controllable items | |
|---|---|
 | 《Transfer block》 ・ Registration of stream to be played ・ Registration of stream to be played next ・ Transfer of stream data ・ Forced switching of video |
 | 《Decode block》 -Start decoding-Stop decoding-Clear data in the decoder buffer |
 | 《Display block》 ・ Switching decoding timing ・ Setting and canceling video pauses ・ Setting and canceling video freezes ・ Switching output destinations |

If the decoding is instructed to stop while decoding a certain video stream, the decoding of the picture being processed is completed, and the decoding is stopped when the decoder detects the next picture start code.
- Stream A decoding
VBV buffer MPEG frame buffer ┌────┬─┬──┐ ┌────┐ ┌─┬──┬───┬───┐ │ │ | │ → │ Decoder │ → │ | │ │ │ │ └────┴─┴──┘└────┘└─┴──┴───┴───┘ Undecoded ↑↑ │ Decoded │ Start next picture
- Decoding stop instruction
VBV buffer MPEG frame buffer ┌────┬────┐ ┌────┐ ┌─┬──┬───┬───┐ │ │ │ → │ Decoder │ → │ | │ │ │ │ └────┴────┘└────┘└─┴──┴───┴───┘ ↑↑ Start next picture Decoding of the picture in process is complete
- VBV buffer
- The undecoded part of the picture currently being processed and the pre-read data after that remain.
- MPEG frame buffer
- The decoded part of the picture currently being processed and the picture data that has already been decoded remain.
Following the decoded picture in the MPEG frame buffer, the pictures in the subsequent stream can be played smoothly.
If the VBV buffer is erased immediately without waiting for the picture start code, the picture in the process of decoding in the MPEG frame buffer may not be able to complete the processing, resulting in a decoding error.
To avoid this delay, the decoded data in the MPEG frame buffer can be erased at the same time as the VBV buffer.
In the following description, repause is an operation in which the pause switch is open, waits for a certain decoding timing, closes the switch, and opens at the next decoding timing. The same applies to the refreeze and freeze switch.
- Decoding timing switching Specifies the timing of the decoding synchronization signal. You can specify whether to decode by VSYNC synchronization or by host synchronization.
- Setting and releasing the pose of the video Set the pose of the video by opening the pause switch. During the pause, the image data does not flow beyond the pause switch, so the image is not updated. Unpause the video by closing the pause switch.
In addition, slow playback can be performed by specifying the repause interval. - Setting and releasing the video freeze Set the video freeze by opening the freeze switch. During the freeze, the image data is discarded from the freeze switch, so the image is not updated. Unfreeze the video by closing the freeze switch.
In addition, strobe playback can be performed by specifying the refreeze interval. - Switching the output destination Switch the output destination of the image data. VDP2 and host can be set as the output destination.
| Status | Switch status | explanation | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pause | Freeze | |||
| 1 | Normal playback | Closed | Closed | It is playing normally. |
| 2 | Pause | Open | Closed | The video is stopped. The image data is stopped at the pause switch. |
| 3 | Freeze | Closed | Open | The video is stopped. The image data is discarded from the freeze switch. |
| Four | Pause& | Open | Open | The video is stopped. The image data is stopped at the pause switch. Even if the pause is released, it freezes and the video does not resume playing. |
Figure 4.3 State transition diagram of MPEG / Video display block
4.2 MPEG / Audio Decoder
The structure of the MPEG / Audio decoder is shown in Figure 4.4.
| Controllable items | |
|---|---|
 | 《Transfer block》 -Registration of the stream to be played-Registration of the stream to be played next-Transfer of stream data-Switching of streams-Setting of stream number and channel number |
 | 《Decode block》 -Start decoding-Stop decoding-Mute audio |
- Start decoding / Stop decoding
- Audio mute
- Get audio timestamp
- LR channel mute <BR> Mute left and right independently.
- Automatic mute at the start of stream input When a stream is input to the audio decoder, the data (about 100 msec) for the first three audio frames is muted.
When the channel to be played back is set, only the data of that channel is sent to the decoder. Since the data of other channels is discarded according to the transfer of the playback channel, the audio synchronized with the video can be played immediately even if the channel is switched to another channel.
Figure 4.5 shows an example of multilingual playback.
Figure 4.5 Multilingual playback
Buffer partition ┌────┬────┬────┬────┬────┬────┬────┐ ┌────┐ │ CN = 3 │ CN = 2 │ CN = 1 │ CN = 3 │ CN = 2 │ CN = 1 │ CN = 3 │ CN = 1 │ Decoder │ │ France │ English │ Japanese │ French │ English │ Japanese │ French │ → │ │ │ └────┴────┴────┴────┴────┴────┴────┘└────┘ An example of playing Japanese with channel number 1 (CN = 1) is shown. French and English audio data will be discarded as the Japanese data is played.
 ★ PROGRAMMER'S GUIDE ★ CD communication I / F (MPEG part)
★ PROGRAMMER'S GUIDE ★ CD communication I / F (MPEG part)