5.1 Transfer block
A stream number and a channel number can be specified to set a more detailed stream to be decoded. (This function is called "rear aperture".)
The timing of switching may be as follows.
Figure 5.1 Registering the next stream to play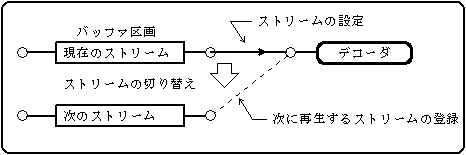
- When a system end code (SEC) is detected
- When the EOR bit is detected
- When the forced switch function is called
| Status | explanation | Transition condition | Transition destination | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Stop | The stream is not registered. | Registration of current stream | Preparation 1 |
2 | Preparation 1 | Waiting for 2 sectors to be stored in the specified buffer partition. | Get decode buffer size | Preparation 2 |
| Cancel the current stream | Stop | |||
3 | Preparation 2 | Waiting for the data for the decode buffer size to be stored in the buffer partition. | Stores the size of the decode buffer | send on |
| Forced transfer instruction | send on | |||
| Cancel the current stream | Stop | |||
4 | Transfer (playback) | The sector data is being transferred to the decoder. (MPEG playback status) | Buffer partition is empty | Resurrection processing |
| Natural switching | switching | |||
| Forced switching | switching | |||
| Natural end | Stop | |||
| forced termination | Stop | |||
5 | switching | Waiting for the beginning of the next stream to be output. | The beginning was output | send on |
| Buffer partition is empty | Resurrection processing | |||
6 | Resurrection processing | Waiting for a sector to be stored in an empty buffer partition. | Stores required sectors | Transfer / Switch * |
Figure 5.2 State transition diagram of the transfer block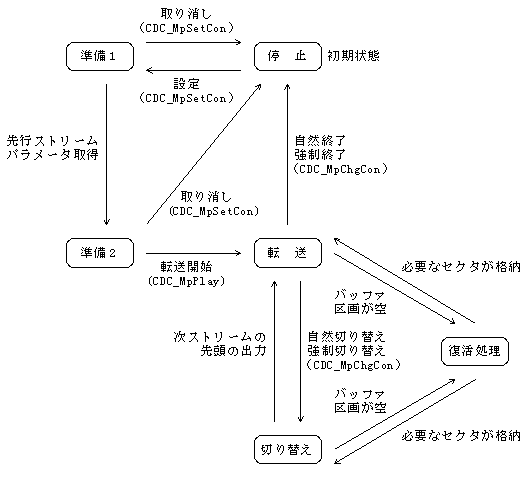
5.2 Stream switching
Figure 5.3 Input order and display order to the decoder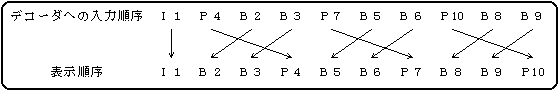
The MPEG / Video decoder has a VBV buffer in front of the decoder and an MPEG frame buffer behind it. The following two methods can be specified as the clearing method (timing and target buffer).
The display-waiting (decoded) MPEG frame buffer is abbreviated as WBC (Write Buffer Control).
Figure 5.4 MPEG video buffer configuration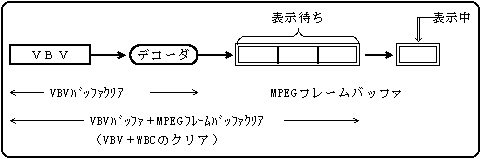
If you simply switch when the picture start is detected, the response will be slightly better, but the frame may be skipped because it may switch at the start of the B picture.
Figure 5.5 Example of switching by P picture start detection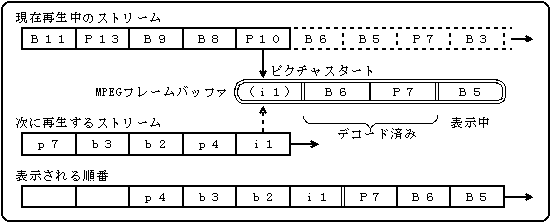
Figure 5.6 Example of switching with B picture start detection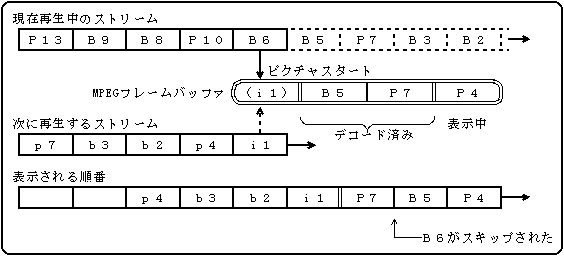
Figure 5.7 MPEG audio buffer configuration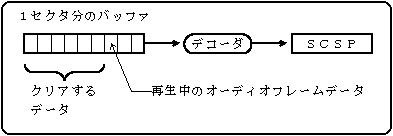
 ★ PROGRAMMER'S GUIDE ★ CD communication I / F (MPEG part)
★ PROGRAMMER'S GUIDE ★ CD communication I / F (MPEG part)