This chapter describes the specific usage of the event structure and event management functions.
By using the idea of events, it is possible to describe a program as a combination of program events (each element in the program), which makes it very easy to understand the flow of the entire program. Furthermore, since each program event can be used in common, the program can be simplified.
10-1. Event structure
Event processing
By using event processing, it is possible to process complicated functions that are executed continuously as a simple list of labels. Also, the execution order can be easily changed as an operation of the label registered as an event.
Therefore, the flow of the entire program can be grasped, and common use of events and simplification of the program can be achieved.
Figure 10-1 Event image
/ * Omitted * /
slInitEvent (); / * Event initialization * /
slSetEvent ((void *) game_demo ); / * Event registration * /
slSetEvent ((void *) game_play );
slSetEvent ((void *) game_over );
slExecuteEvent (); / * Execute event * /
void game_demo (EVENT * evptr) {/ * Execute event 1 (game_demo) * /
::
}
void game_play (EVENT * evptr) {/ * Execute event 2 (game_play) * /
::
}
void game_over (EVENT * evptr) {/ * Execute event 3 (game_over) * /
::
}
/ * Abbreviation * /
| 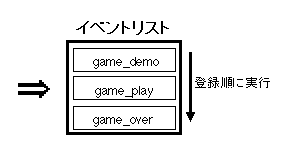 |
In SGL, the event execution order is called the event list.
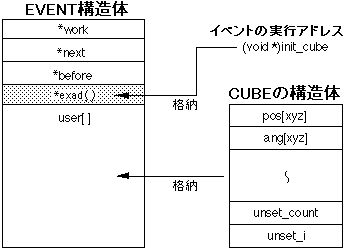
EVENT structure
Figure 10-2 EVENT structure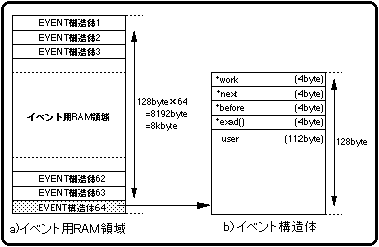
* work: The start address of the WORK structure for user area extension.
* next: The start address of the next event to be executed.
* before: The start address of the event that is executed immediately before.
* exit (): The start address of the area where the function to be executed as an event is stored.
user []: User area for storing variables used by event-registered functions.
It is also possible to expand the user area using work.
Event list
A list is a series of events that are concatenated and executed by “* next” and “* before” reserved in the event structure, and are called an event list.
In addition, events that are executed continuously in the event list do not necessarily have to be stored in the event RAM area continuously, and if the pointers are concatenated with "* next" and "* before", It runs continuously.
Figure 10-3 Event list structure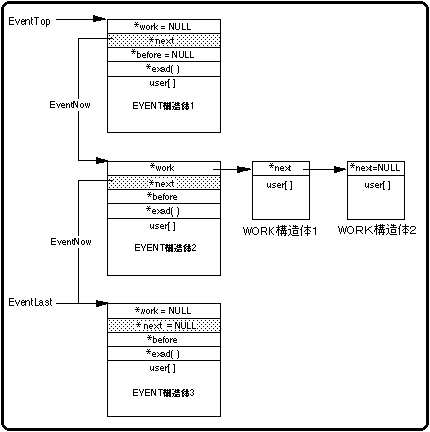
The executed event passes the value of the pointer “* next” in the EVENT structure to the EventNow variable, and the system executes the EVENT structure starting from the address pointed to by “EventNow” next. The system executes the events in order according to “EventNow”, and ends the event execution process when the value pointed to by “* next” becomes NULL (there is no event to follow).
The EventLast variable points to the start address of the EVENT structure registered at the end of the list and is used when adding / registering an event. In addition, the EventLast variable is changed only when "slSetEvent", "slSetEventNext", and "slCloseEvent" are executed in the library functions.
“* Before” is used when inserting / registering / deleting an event.
10-2. Event processing using SGL function
Event initialization
caution | If event processing is used without executing event initialization, it will be inconsistent with uninitialized buffers, event lists, etc., and in the worst case, the CPU may stop. (Detail is |
|---|
Creating an event list
Events are added to the event list by the event registration library function “slSetEvent” as shown in Figure 10-4.
The registered events are sequentially registered at the end of the event list, and are executed in order from the beginning of the event list by the event execution library function "slExecuteEvent".
Figure 10-4 Creating an event list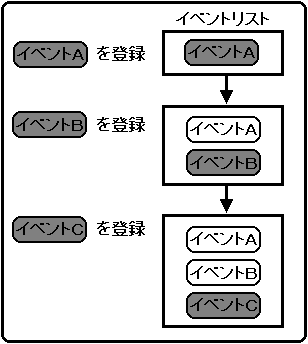
The function “slSetEvent” returns the start address of the registered EVENT structure as a return value. If registration of the event fails, NULL is returned.
Event format
● Event format ●void function_name (EVENT * evptr) {execute_contents} ↑ ↑ ↑ | | Event execution content | Start address of EVENT structure Event name
The EVENT structure stores the execution address of the event to be registered and the structure for variables used in the event, and manages the event with these two.
/ * Omitted * /
slSetEvent ((void *) init_cube);
slExecuteEvent ();
typedef struct cube {FIXEDpos [xyz];
ANGLE ang [xyz]
;
::
Sint16 unset_count;
Sint16 unset_i;
} CUBE;
void init_cube (EVENT * evptr)
{
CUBE * cubeptr;
cubeptr = (CUBE *) evptr-> user;
cubeptr-> pos [x] = pos_x;
::
cubeptr-> unset_count = 0;
disp_cube (evptr);
}
/ * Abbreviation * /
|  |
About the structure for variables in the event
<The defined in-event variable structure is stored in the user area (112 bytes) in the EVENT structure when the event is registered (the storage work is done by the user), and is used at any time after that when the event is executed.
Therefore, the in-event variable structure cannot be set beyond the size of the user area (112 bytes) in which the structure is stored.
<However, if you want to use more variables, extend the user area using a WORK structure, etc., and store and use the in-event variable structure by dividing it to fit the size of the user area. (For how to extend the user area, refer to "10-4: Extending the user area").
Event execution
The library function “slExecuteEvent” is used to execute the event.
Figure 10-7 Executing an event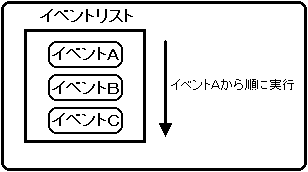
10-3. Change the event list
Add event
The event is added to the end of the event list.
To add an event, use the same library function “slSetEvent” that was used for event registration.
Figure 10-8 Adding an event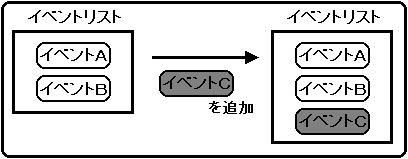
The function “slSetEvent” returns the start address of the registered EVENT structure as a return value.
If registration of the event fails, NULL is returned.
Insert event
The event will be inserted after the specified event.
Use the library function “slSetEventNext” to insert an event.
Figure 10-9 Inserting an event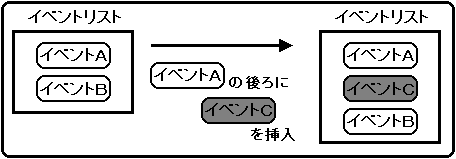
The function “slSetEventNext” returns the start address of the registered EVENT structure as a return value.
If registration of the event fails, NULL is returned.
Delete event
Use the library function “slCloseEvent” to delete an event.
Figure 10-10 Deleting an event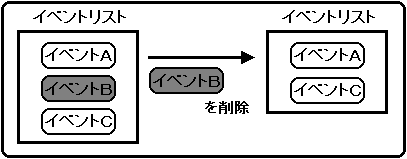
At the same time, if the member "work" of the specified event is not NULL, all attached works are returned to the system assuming that there is a work list.
Assign the start address of the EVENT structure to be deleted to the parameter.
Also, the function “slCloseEvent” does not check whether the area to be returned is a registered EVENT structure. Therefore, if you accidentally return the extended user area to the system, you will not know.
In this case, various problems may occur, and in the worst case, the CPU may stop (see "10-5: Precautions for event processing" for details).
Change the event list during event execution
Figure 10-11 Modifying the event list during event execution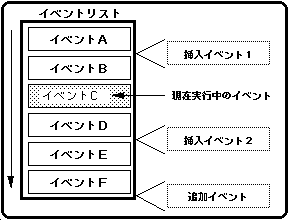
10-4. Expansion of user area
In such a case, SGL can extend the user area and use it.
There are two ways to expand the user area, one is to use an extension-only area called work, and the other is to acquire an extension area of the same size as the EVENT structure from the event RAM area.
Extension of user area using work area
A work is defined as a WORK structure (64 bytes) in the work RAM area, and up to 256 works can be used.
The size of the user area that can be expanded per work is 60 bytes.
The remaining 4 bytes of the WORK structure are used to address the WORK structure to be concatenated.
Figure 10-12 WORK structure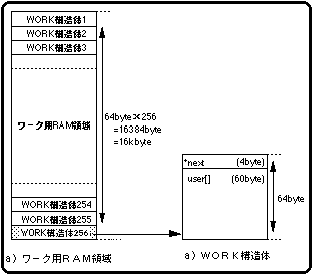
* next: The start address of the WORK structure that you want to connect as a chain structure.
If there is no work to follow as a chain structure, NULL is assigned.
user []: Extended user area (60 bytes).
In addition, the work can further expand the user area by acquiring the work again in the WORK structure. At this time, by substituting the start address of the WORK structure to be linked to “* next” in the WORK structure, the linked work can be made into a chain structure.
When there is no WORK structure that follows as a chain structure, NULL is assigned to “* next”.
Figure 10-13 Work concatenation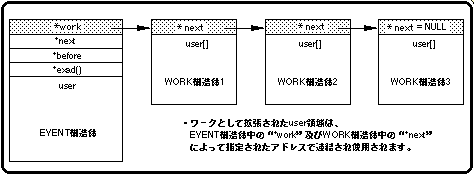
The function “slGetWork” returns the WORK structure address value of the allocated work area as a return value. If space allocation fails, the function returns NULL.
About the operation of the concatenated WORK structure by releasing the EVENT structure
However, for the work connected by "* work" and "* next", the work is returned and released to the system at the same time by releasing the event, but the work connected from the user area releases the event. Does not release the WORK structure.
Therefore, the WORK structure connected from the user area must be returned / released to the system by the library function “slReturnWork” when the event is released.
Expansion of user area using event area
However, since the area originally allocated for one event is used as the user area, the maximum number of events that can be registered will be reduced by that amount.
Figure 10-14 Expanding the user area using the event RAM area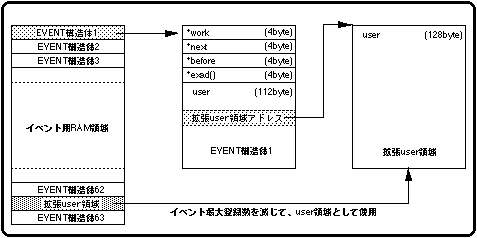
The function “slGetEvent” returns the start address of the allocated RAM area as a return value.
If space allocation fails, the function returns NULL.
Assign the start address of the RAM area to be returned to the parameter.
Also, the function “slReturnEvent” does not check if the area to be returned is an extended user area. Therefore, even if you mistakenly return the EVENT structure registered as an event to the system, you will not know. In this case, various problems will occur, and in the worst case, the CPU may stop (see “10-5: Precautions for event processing” for details).
10-5. Precautions for event processing
- Return of area <BR> The EVENT structure specified by the function "slReturnEvent" is returned to the system.
- Event list
The EVENT structure is not released as an event and therefore remains in the event list. - Since the new event registration <BR> area is systematically free, it can be freely used by using the function "slSetEvent" or the like.
- Inconsistency in chain structure <BR> Although it is registered in the event list, the contents of the EVENT structure are rewritten because the area is in a free state, which causes a problem in the chain structure.
- CPU stop <BR> The chain structure becomes inconsistent, and in the worst case, the CPU stops.
Figure 10-15 Incorrect event operation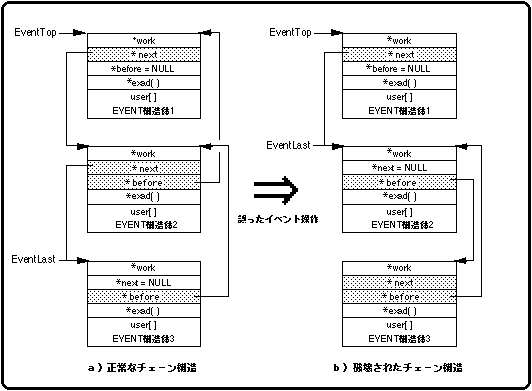
10-6. Event processing flow
Flow 10-1 Event processing flow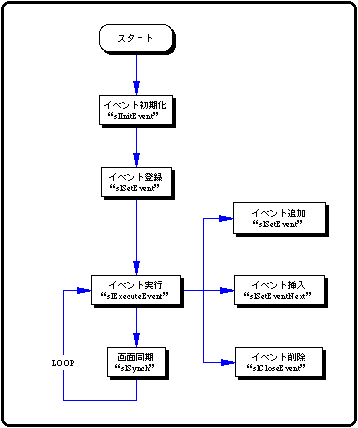
10-7. Example of using the event
/ * ------------------------------------------------ ---------------------- * /
/ * Event Demo * /
/ * ------------------------------------------------ ---------------------- * /
#include "sgl.h"
void ss_main (void)
{
slInitSystem (TV_320x224, NULL, 1);
slPrint ("Sample program 10", slLocate (9,2));
set_event ();
while (-1) {
slExecuteEvent ();
slSynch ();
}
}
Flow 10-2 sample_10: Main loop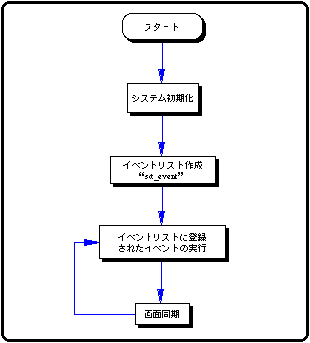
#include "sgl.h"
extern PDATA PD_CUBE;
#define POS_X toFIXED (0.0)
#define POS_X_UP 200.0
#define POS_Y toFIXED (20.0)
#define POS_Z toFIXED (270.0)
#define POS_Z_UP 50.0
#define SET_COUNT 500
static void init_cube2 (EVENT *);
typedef struct cube {
FIXED pos [XYZ];
ANGLE ang [XYZ];
ANGLE angx, angz;
ANGLE angx_up, angz_up;
PDATA * poly;
Sint16 set_count, set_i;
Sint16 unset_count, unset_i;
} CUBE;
static void disp_cube (EVENT * evptr)
{
CUBE * cubeptr;
cubeptr = (CUBE *) evptr-> user;
slPushMatrix ();
{
slTranslate (cubeptr-> pos [X], cubeptr-> pos [Y], cubeptr-> pos [Z]);
cubeptr-> pos [X] = POS_X + POS_X_UP * slSin (cubeptr-> angx);
cubeptr-> pos [Y] = cubeptr-> pos [Y];
cubeptr-> pos [Z] = POS_Z + POS_Z_UP * slCos (cubeptr-> angz);
cubeptr-> angx + = cubeptr-> angx_up;
cubeptr-> angz + = cubeptr-> angz_up;
slRotY (cubeptr-> ang [Y]);
slRotX (cubeptr-> ang [X]);
slRotZ (cubeptr-> ang [Z]);
cubeptr-> ang [X] + = DEGtoANG (5.0);
cubeptr-> ang [Y] + = DEGtoANG (5.0);
cubeptr-> ang [Z] + = DEGtoANG (5.0);
slPutPolygon (cubeptr-> poly);
}
slPopMatrix ();
cubeptr-> set_count-= cubeptr-> set_i;
if (cubeptr-> set_count <0) {
slSetEvent ((void *) init_cube2);
cubeptr-> set_count = SET_COUNT;
}
cubeptr-> unset_count-= cubeptr-> unset_i;
if (cubeptr-> unset_count <0) slCloseEvent (evptr);
}
static void init_cube1 (EVENT * evptr)
{
CUBE * cubeptr;
cubeptr = (CUBE *) evptr-> user;
cubeptr-> pos [X] = POS_X;
cubeptr-> pos [Y] = POS_Y;
cubeptr-> pos [Z] = POS_Z;
cubeptr-> ang [X] = cubeptr-> ang [Y] = cubeptr-> ang [Z] = DEGtoANG (0.0);
cubeptr-> angx = cubeptr-> angz = DEGtoANG (0.0);
cubeptr-> angx_up = cubeptr-> angz_up = DEGtoANG (0.0);
cubeptr-> set_count = SET_COUNT;
cubeptr-> set_i = 1;
cubeptr-> unset_count = 0;
cubeptr-> unset_i = 0;
cubeptr-> poly = & PD_CUBE;
evptr-> exit = (void *) disp_cube;
disp_cube (evptr);
}
static void init_cube2 (EVENT * evptr)
{
CUBE * cubeptr;
cubeptr = (CUBE *) evptr-> user;
cubeptr-> pos [X] = POS_X;
cubeptr-> pos [Y] = POS_Y-toFIXED (50);
cubeptr-> pos [Z] = POS_Z + POS_Z_UP;
cubeptr-> ang [X] = cubeptr-> ang [Y] = cubeptr-> ang [Z] = DEGtoANG (0.0);
cubeptr-> angx = cubeptr-> angz = DEGtoANG (0.0);
cubeptr-> angx_up = cubeptr-> angz_up = DEGtoANG (3.0) * (-1);
cubeptr-> set_count = 0;
cubeptr-> set_i = 0;
cubeptr-> unset_count = SET_COUNT / 2;
cubeptr-> unset_i = 1;
cubeptr-> poly = & PD_CUBE;
evptr-> exit = (void *) disp_cube;
disp_cube (evptr);
}
static void init_cube3 (EVENT * evptr)
{
CUBE * cubeptr;
cubeptr = (CUBE *) evptr-> user;
cubeptr-> pos [X] = POS_X;
cubeptr-> pos [Y] = POS_Y + toFIXED (50);
cubeptr-> pos [Z] = POS_Z + POS_Z_UP;
cubeptr-> ang [X] = cubeptr-> ang [Y] = cubeptr-> ang [Z] = DEGtoANG (0.0);
cubeptr-> angx = cubeptr-> angz = DEGtoANG (0.0);
cubeptr-> angx_up = cubeptr-> angz_up = DEGtoANG (3.0);
cubeptr-> set_count = 0;
cubeptr-> set_i = 0;
cubeptr-> unset_count = 0;
cubeptr-> unset_i = 0;
cubeptr-> poly = & PD_CUBE;
evptr-> exit = (void *) disp_cube;
disp_cube (evptr);
}
void * event_tbl [] = {
init_cube1,
init_cube2,
init_cube3
};
void set_event ()
{
EVENT * evptr;
void ** exptr;
Uint16 cnt;
slInitEvent ();
for (exptr = event_tbl, cnt = sizeof (event_tbl) / sizeof (void *); cnt-> 0;) {
evptr = slSetEvent (* exptr ++);
}
}
The event execution content differs between the first loop and the second and subsequent loops.
In the figure, the left is the execution content of the first event, and the right is the execution content of the second and subsequent events.
Flow 10-3 samp_10: Event execution content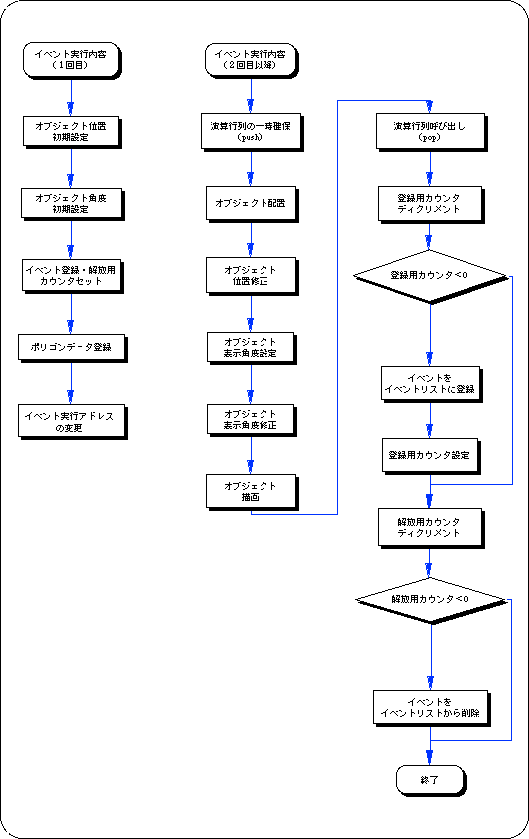
Appendix SGL library functions that appeared in this chapter
Functional type | Seki several people | Parameter | function |
|---|---|---|---|
| void | slInitEvent | void | Initialize the event |
| EVENT | * slSetEvent | void (* func) () | Event list Register / add events |
| void | slExecuteEvent | void | Executes the events registered in the list in order |
| EVENT | * slSetEventNext | EVENT * evptr, void (* func) () | Inserts / registers a new event immediately after the specified event |
| void | slCloseEvent | EVENT * evptr | Deletes the event from the event list, and at the same time returns and releases the attached work to the system. |
| WORK | * slGetWork | void | Secure work area |
| void | slReturnWork | WORK * wkptr | Return / release the work area |
| EVENT | * slGetEvent | void | Allocate a RAM area of the same size as the event in the event RAM |
| void | slReturnEvent | EVENT * evptr | The area secured by the function "slGetEvent" is returned / released to the system. |
 ★ SGL User's Manual ★ PROGRAMMER'S STRUCT
★ SGL User's Manual ★ PROGRAMMER'S STRUCT