This chapter describes the procedure and precautions for outputting sound with Sega Saturn using the sound control library.
14-1. Overview of sound control
The master CPU and sound CPU exchange functions through a RAM called a command buffer. Since the function is issued by the sound control library, the user can control the sound without being aware of the interaction between the CPUs.
There are PCM and CD sound sources that can be used with Sega Saturn, and the sound driver controls the PCM sound source.
┏━━━━━━┓ ┏━━━━━━┓ ┏━━━━━━┓ ┃Sound ┃┃┃┃┃┃ ┃ Library ┃ ← → ┃ Master ┃ ← → ┃ Slave ┃ ┠──────┨ ┃ CPU ┃ ┃ CPU ┃ ┃ ┃ ┃ ┃ ┃ ┃ ┃ ┃ ┗━━━━━━┛ ┗━━━━━━┛ ┃ ┃ ↑ ┃ ┃ ↓ ┃ ┃ ┏━━━━━━┓ ┃ ┃ ┃ Sound ┃ ┃ ┃ ┃ Driver ┃ ┏ ━━━━━━━━┓ ┃ ┃ ┠ ────── ┨ ┃ Sound CPU ┃ ┗━━━━━━┛ ┃ Command ┃ ← → ┃ MC68000 ┃ ┃ Buffer ┃ ┃ ┃ ┃ ┃ ┗━━━━━━━━┛ ┠──────┨ ↓ ┃ ┃ ┏━━━━━┓ ┃Sound ┃┃PCM sound source ┃ → speaker ┃data ┃┗━━━━━┛ ┗━━━━━━┛ Shared RAM
14-2. Sound driver settings
┏━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┓ ┃Sound driver set ┃ ┃ and start MC68000 ┃ ┗━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┛ ↓ ┏━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┓ ┃Sound data set ┃ ┗━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┛ ↓ ┏━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┓ ┃BGM performance / sound effect, ┃ ┃ PCM sound source control ┃ ┗━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┛
Set sound driver and start MC68000
Normally,
slInitSound (drv, sizeof (drv), maptbl, sizeof (maptbl));
Use like.
- Reset MC68000
- Memory area of MC68000 0 clear up to 0xB000
- Transfer of driver program (size from address 0)
- Transfer of map data (size from address 0xA000)
- Registration of memory area for PCM playback
- Start of MC68000
- Registration of map data
Set of sound data
┌ ┐ │ slDMACopy (sounddat, (void *) 0x25a0b000, sizeof (sounddat)); │ │ slDMAWait (); │ └ ┘
BGM performance
Song: Song (sound effect) number Prio: Priority when using the sound source Volume: Volume Rate: Time to reach Volume
slBGMTempo (Sint16 Tempo); / * Tempo change * / slBGMFade (Uint8 Volume, Uint8 Rate); / * Change volume * / slBGMOff (); / * Stop playing * / slBGMPause (); / * Pause playing * / slBGMCont (); / * Resume playing * / slBGMStat (); / * Check if playing * /
Sound effect output
Song: Song (sound effect) number Prio: Priority when using the sound source Volume: Volume Pan: Sorting the left and right volumes
Left: -128 << 0 >> +127: Right
slSequenceTempo (Uint8 Seqnm, Sint16 Tempo); / * Change tempo * / slSequenceFade (Uint8 Seqnm, Uint8 Volume, Uint8 Rate); / * Change volume * / slSequencePan (Uint8 Seqnm, Uint8 Pan); / * Change the direction of occurrence * / slSequenceOff (Uint8 Seqnm); / * Stop the sequence * / slSequencePause (Uint8 Seqnm); / * Pause the sequence * / slSequenceCont (Uint8 Seqnm); / * Resume the paused sequence * / slSequenceStat (Uint8 Seqnm); / * Check if the sequence is playing * /
Sound effect output using PCM sound source
- [Sint 8 slPCMOn (PCM * pdat, void * data, Uint32 size);]
- Start playing with the PCM sound source.
pdat: PCM type structure data such as PCM stream playback mode data: PCM stream sound source data size: PCM stream data size
The PCM type structure data has the following configuration and is used to specify the playback parameters of the PCM stream.
Figure 14-4 PCM type structure data
typedef struct {
Uint8 mode; / * Mode * /
Uint8 channel; / * PCM Channel Number * /
Uint8 level; / * 0 ~ 127 * /
Sint8 pan; / * -128 ~ +127 * /
Uint16 pitch;
Uint8 eflevelR; / * Effect level for Right (nomo) 0 ~ 7 * /
Uint8 efselectR; / * Effect select for Right (mono) 0 ~ 15 * /
Uint8 eflevelL; / * Effect level for Left (mono) 0 ~ 7 * /
Uint8 efselectL; / * Effect select for Left (mono) 0 ~ 15 * /
} PCM;
mode: Specify _Stereo or _Mono, _PCM16Bit or _PCM8Bit channel: PCM playback channel (set by this function)
level: Volume pan: Volume left and right distribution pitch: Playback rate (pitch changes)
eflevelR: Degree of applying effects (for right channel)
efselectR: Effect number (for right channel)
eflevelL: Degree of applying effect (for left channel)
efselectL: Effect number (for left channel)
slPCMOff (PCM * pdat); / * Stop playing * / slPCMParmChange (PCM * pdat); / * Change parameters * / slPCMStat (PCM * pdat); / * Check if the specified PCM channel is playing * /
Functions that affect the overall sound output
slSndVolume (Uint8 Volume); / * Overall volume * / slSoundAllOff (); / * Stop all sound sequences * / slDSPOff (); / * Stop DSP for effect * / slSndMixChange (Uint8 Tbank, Uint8 Mixno); / * Mixer switching * / slSndMixParmChange (Uint8 Effect, Uint8 Level, Uint8 Pan); / * Change mixer parameters * /
14-3. Memory map
25A00000┏━━━━━━━━━━━━┓
┃ ┃
┃ Exception vector etc. ┃
┃ ┃
25A00500 ┣━━━━━━━━━━━━┫
┃ ┃
┃Current map data ┃
┃ ┃
25A00700 ┣━━━━━━━━━━━━┫
┃ ┃
┃ Command buffer ┃
┃ ┃
25A00800 ┣━━━━━━━━━━━━┫
┃ ┃
┃Sound driver ┃
┃ ┃
25A0A000 ┣━━━━━━━━━━━━┫
┃ ┃
┃ Map data ┃
┃ ┃
25A0B000 ┣━━━━━━━━━━━━┫
┃ ┃
┃Tone, sequence ┃
┃ ┃
25A78000 ┣━━━━━━━━━━━━┫
┃ ┃
┃ PCM playback buffer ┃
┃ ┃
25A7FFFF ┗━━━━━━━━━━━━┛
14-4. Sample program
Sample program for BGM and sound effect playback test
Bank Song Contents ------ ------ ------- 0 0 songs (no loops) 1 song (with loop) 10 Pass (C3) 1 Pass (D3) 2 Pass (E3) 3 Pass (F3) 4 Pass (G3) 5 Pass (A3) 6 Pass (B3) 7 Pass (C4) 20 Ye 30 Long violin sound 1 Short violin sound (loop)
main.c
Flow 14-1 sampsnd1: BGM and sound effect playback test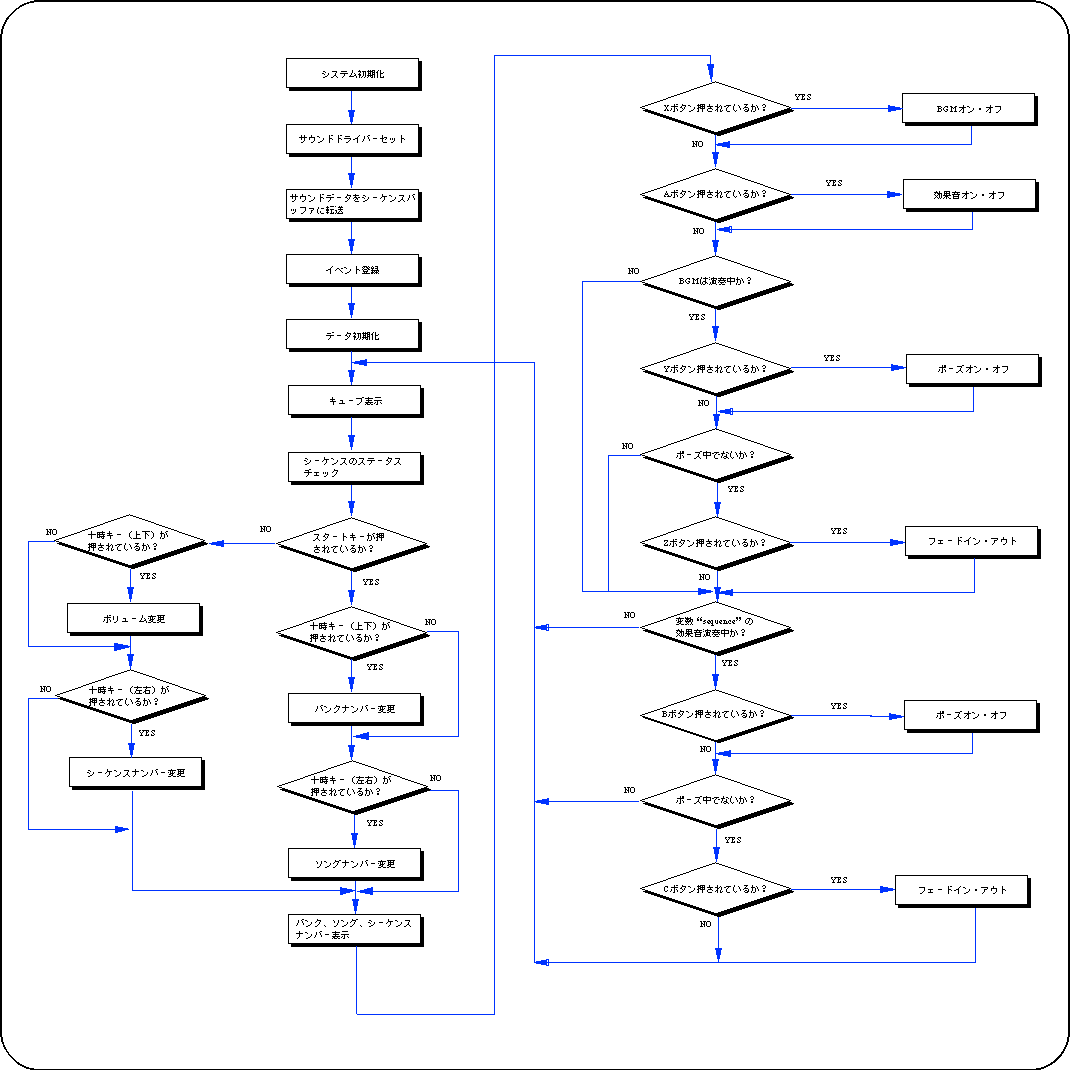
Sample program for PCM sound source playback test
There are three types of sample data for PCM sound sources: 16-bit stereo, 8-bit stereo, and 16-bit monaural, which are played back by inputting the X, Y, and Z buttons, respectively.
main.c
Flow 14-2 sampsnd2: PCM sound source playback test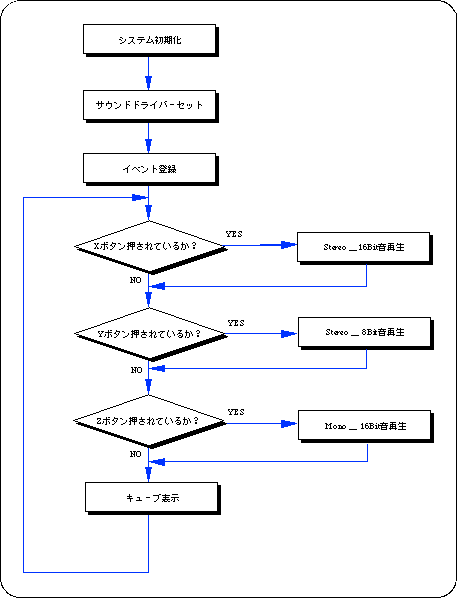
Appendix Sound library functions that appeared in this chapter
Functional type | Seki several people | Parameter | function |
|---|---|---|---|
| void | slInitSound | void * drv, Uint32 drvsz, void * map, Uint32 mapsz | Sound driver set and sound control CPU initialization |
| Bool | slBGMOn | Uint16 Song, Uint8 Prio, Uint8 Volume, Uint8 Rate | Start of BGM performance |
| Bool | slBGMTempo | Sint16 Tempo | Change of BGM playing speed |
| Bool | slBGMFade | Uint8 Volume, Uint8 Rate | Change BGM performance volume |
| Bool | slBGMOff | void | Stop playing BGM |
| Bool | slBGMPause | void | Pause BGM performance |
| Bool | slBGMCont | void | Paused BGM performance resumed |
| Bool | slBGMStat | void | Check during BGM playback |
| Uint8 | slSequenceOn | Uint16 Song, Uint8 Prio, Uint8 Volume, Uint8 Rate | Start generating the specified sound effect |
| Bool | slSequenceTempo | Uint8 Seqnm, Uint16 Tempo | Change the speed of the specified sound effect |
| Bool | slSequenceFade | Uint8 Seqnm, Uint8 Volume, Uint8 Rate | Change the volume of the specified sound effect |
| Bool | slSequencePan | Uint8 Seqnm, Uint8 Pan | Change the direction of the specified sound effect |
| Bool | slSequenceOff | Uint8 Seqnm | Stop generating the specified sound effect |
| Bool | slSequencePause | Uint8 Seqnm | Pauses the generation of the specified sound effect |
| Bool | slSequenceCont | Uint8 Seqnm | Resuming sound effects during pause |
| Bool | slSequenceStat | Uint8 Seqnm | Check during playback of the specified sound effect |
| Sint8 | slPCMOn | PCM * pdat, void * data, Uint32 size | Start playing with PCM sound source |
| Bool | slPCMOff | PCM * pdat | Stop playing with PCM sound source |
| Bool | slPCMParmChange | PCM * pdat | Change parameters for PCM playback |
| Bool | slPCMStat | PCM * pdat | Check during playback of the specified PCM channel |
| Bool | slSndVolume | Uint8 Volume | Overall volume set |
| Bool | slSoundAllOff | void | Stop playing all sound sequences |
| Bool | slDSPOff | void | Stop playing DSP |
| Bool | slSndMixChange | Uint8 Tbank, Uint8 Mixno | Switching the mixer corresponding to the tone bank |
| Bool | slSndMixParmChange | UInt Effect, Uint8 Level, Uint8 Pan | Mixer parameter change |
 ★ SGL User's Manual ★ PROGRAMMER'S STRUCT
★ SGL User's Manual ★ PROGRAMMER'S STRUCT