13-1. Features of backup library
device
| Device number | Device type |
|---|---|
| 0 | Built-in memory cartridge |
| 1 | Memory cartridge or parallel interface |
Figure 13-1 Device configuration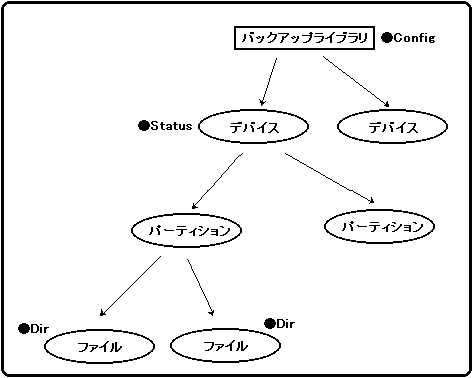
File
The file information setting at the time of file creation is the responsibility of the user at the time of file creation, and the backup library itself does not create the file information.
Library expansion
caution | The backup library destroys data if processing is interrupted while writing data. Therefore, when initializing, formatting, writing, or deleting the backup library, use “slResetDisable ()” (peripheral function) in the system library to disable the reset button. |
|---|
13-2. Basic processing flow
- 1) Initialization [BUP_Init ()]
- Reads the backup library from BOOTROM and expands it to the specified address space. Returns each device information at that time.
- 2) Select partition [BUP_SelPart ()]
- Specify the partition of the device to be used. The default partition is number 0 (internal memory cartridge).
- 3) Get status [BUP_Stat ()]
- Get the status of the device you want to read and write. When writing, specify the size of the data you want to write in bytes. You can tell whether it is writable by the return value.
- 4) Format [BUP_Format ()]
- If the device you want to use is unformatted due to the status acquisition, you need to format it. The format range is the specified partition of the specified device.
- 5) Get directory information [BUP_Dir ()]
- Get the directory information by specifying the file name (or for all files). If you want information about all files, specify NULL for the file name.
- 6) Write data [BUP_Write ()]
- Specify the device and write the file. The file information required at that time is created by the user.
- 7) Data query [BUP_Verify ()]
- Specify the device and inquire about the written file.
- 8) Read data [BUP_Read ()]
- Specify the device to read the file.
- 9) Delete data [BUP_Delete ()]
- Specify the device and delete the file.
- 10) Expansion of date data [BUP_GetDate ()]
- Compresses into file information and expands the stored date data.
- 11) Compression of date data [BUP_SetDate ()]
- Compress to store date data in file information.
13-3. Sample program
Flow 13-1 Sample program that uses the backup library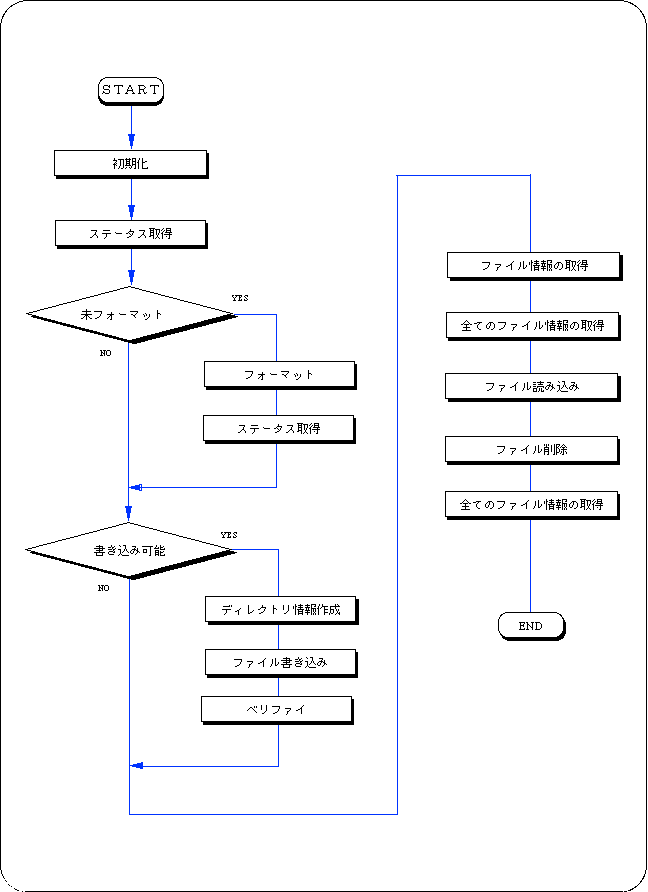
#include "sgl.h"
#define BUP_START_ADDR 0x6070000
#include "sega_bup.h"
#define FILE_NAME "FILE_NAME01"
#define BACKUP_DEVICE (Uint32) 0
#define TEST_DATA "It's a pen"
#define TEST_SIZE 10
#define DIR_SIZE 8
#define HEX2DEC (x) ((0x0f & (x)) + ((x) >> 4) * 10)
/ ***************************************************** ** **
sample for backupram
****************************************************** * /
Uint32 BackUpRamWork [2048 + 30];
void BackUpInit (BupConfig cntb [3])
{
slResetDisable ();
BUP_Init ((Uint32 *) BUP_START_ADDR, BackUpRamWork, cntb);
slResetEnable ();
}
Sint32 BackUpWrite (Uint32 device, BupDir * dir, Uint8 * data, Uint8 sw)
{
Sint32 ret;
SmpcDateTime * time;
BupDate date;
if (! dir-> date) {
time = & (Smpc_Status-> rtc);
date.year = (Uint8) (slDec2Hex ((Uint32) time-> year)-1980); / * Modify KT * /
date.month = (Uint8) (time-> month & 0x0f);
date.week = (Uint8) (time-> month >> 4);
date.day = (Uint8) (slDec2Hex ((Uint32) time-> date)); / * Modify KT * /
date.time = (Uint8) (slDec2Hex ((Uint32) time-> hour)); / * Modify KT * /
date.min = (Uint8) (slDec2Hex ((Uint32) time-> minute)); / * Modify KT * /
dir-> date = BUP_SetDate (& date);
}
slResetDisable ();
ret = BUP_Write (device, dir, data, sw);
slResetEnable ();
return (ret);
}
Sint32 BackUpDelete (Uint32 device, Uint8 * filename)
{
Sint32 ret;
slResetDisable ();
ret = BUP_Delete (device, filename);
slResetEnable ();
return (ret);
}
Sint32 BackUpFormat (Uint32 device)
{
Sint32 ret;
slResetDisable ();
ret = BUP_Format (device);
slResetEnable ();
return (ret);
}
void ss_main ()
{
BupConfig conf [3];
BupStat sttb;
BupDir dir, dirs [DIR_SIZE];
BupDate datetb, date;
Uint8 * time;
Sint32 status;
Uint8 buf [256];
int i, lin = 4;
slInitSystem (TV_352x224, (TEXTURE *) NULL, 1);
slPrint ("Sample program Backup Library", slLocate (9,2));
slGetStatus ();
for (i = 0; i <100; i ++)
{
slSynch ();
}
BackUpInit (conf);
if ((status = BUP_Stat (BACKUP_DEVICE, 10, & sttb)) == BUP_UNFORMAT)
{
status = BackUpFormat (BACKUP_DEVICE);
slPrint ("Formatting device", slLocate (10, lin));
BUP_Stat (BACKUP_DEVICE, TEST_SIZE, & sttb);
}
if (sttb.freeblock> 0)
{
strncpy (dir.filename, FILE_NAME, 11);
strncpy (dir.comment, "Test desu", 10);
dir.language = BUP_ENGLISH;
dir.datasize = TEST_SIZE;
dir.date = 0;
slPrint ("Writing file.", SlLocate (10, ++ lin));
slPrint ("Filename =", slLocate (13, ++ lin));
slPrint (FILE_NAME, slLocate (23, lin));
status = BackUpWrite (BACKUP_DEVICE, & dir, (Uint8 *) TEST_DATA, OFF);
status = BUP_Verify (BACKUP_DEVICE, (Uint8 *) FILE_NAME, (Uint8 *) TEST_DATA);
}
status = BUP_Dir (BACKUP_DEVICE, (Uint8 *) FILE_NAME, DIR_SIZE, dirs);
status = BUP_Dir (BACKUP_DEVICE, (Uint8 *) "", DIR_SIZE, dirs);
for (i = 0; i <status && i <10; i ++)
{
char cmnt [11] = "Dirs =";
cmnt [6] = (char) (i + 20);
slPrint ("Dirs =", slLocate (10, ++ lin));
slPrint (dirs [i] .filename, slLocate (20, lin));
}
status = BackUpWrite (BACKUP_DEVICE, & dir, (Uint8 *) TEST_DATA, OFF);
status = BUP_Read (BACKUP_DEVICE, (Uint8 *) FILE_NAME, buf);
slPrint ("Reading file.", SlLocate (10, ++ lin));
slPrint ("Filename =", slLocate (13, ++ lin));
slPrint (FILE_NAME, slLocate (23, lin));
#if 0
status = BackUpDelete (BACKUP_DEVICE, (Uint8 *) FILE_NAME);
status = BUP_Dir (BACKUP_DEVICE, (Uint8 *) "", DIR_SIZE, dirs);
slPrint ("Deleting =", slLocate (10, ++ lin));
slPrint ("Filename =", slLocate (13, ++ lin));
slPrint (FILE_NAME, slLocate (23, lin));
#endif
for (i = 0; i <status && i <10; i ++)
{
char cmnt [11] = "Dirs =";
cmnt [6] = (char) (i + 20);
slPrint ("Dirs =", slLocate (10, ++ lin));
slPrint (dirs [i] .filename, slLocate (20, lin));
}
for (;;)
{
slSynch ();
}
}
Appendix Backup library function
For a detailed reference of the function, refer to PROGRAMMER'S GUIDE VOL.1.
number | Seki several people | function |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | BUP_Init | Backup library initialization |
| 2 | BUP_SelPart | Partition selection |
| 3 | BUP_Format | Formatting |
| Four | BUP_Stat | Get status |
| Five | BUP_Write | Writing data |
| 6 | BUP_Read | Read data |
| 7 | BUP_Delete | Delete data |
| 8 | BUP_Dir | Get directory information |
| 9 | BUP_Verify | Display data |
| Ten | BUP_GetDate | Deployment of date data |
| 11 | BUP_SetDate | Compression of date data |
 ★ SGL User's Manual ★ PROGRAMMER'S STRUCT
★ SGL User's Manual ★ PROGRAMMER'S STRUCT