 ★ SOUND Manual ★ Sound Driver Programmer's Guide
★ SOUND Manual ★ Sound Driver Programmer's Guide Sound System Hardware
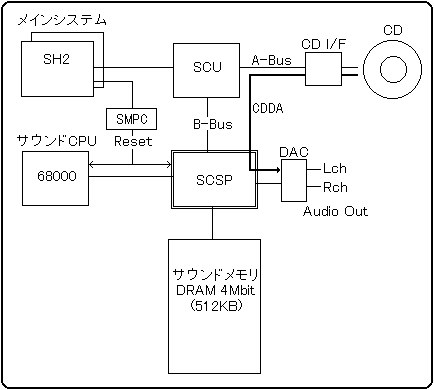
The sound system is centered on the sound source LSI, and the sound CPU and 512KB sound memory, the main system and the CD interface, etc. are connected. The main system can access the entire IO space of the sound memory and SCSP via the SCU, and can control the stop (reset) and restart (reset release) of the sound CPU through the SMPC.
The most important of these is the sound memory, which controls everything in the sound system, including sound driver execution, data management, sound source data storage, and communication between systems.
A sound driver is a sound control program for pronouncing songs and sound effects. The program is stored in sound memory and operates independently of the main system. Therefore, songs and sound effects can be played from the main system simply by issuing commands.
Both the sound driver and sound data are stored in the sound memory, so once the power is turned off, all of them will be lost. Therefore, the main system must start the sound driver every time the power is turned on. Since the sound CPU at power-on is stopped by the reset signal, first transfer the sound driver to the sound memory and then release the reset signal. This will launch the sound driver and allow you to play songs and sound effects.
Sound memory has a system area and a data area. The system area is a fixed area for sound driver operation and system management, and the data area is a variable area (variable mapping) for storing sound source data and internal processing of the DSP.
Sound memory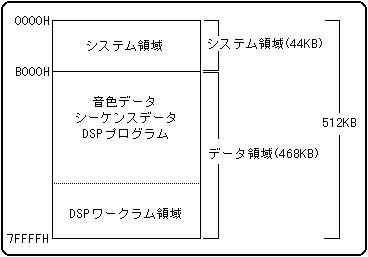
 ★ SOUND Manual ★ Sound Driver Programmer's Guide
★ SOUND Manual ★ Sound Driver Programmer's Guide