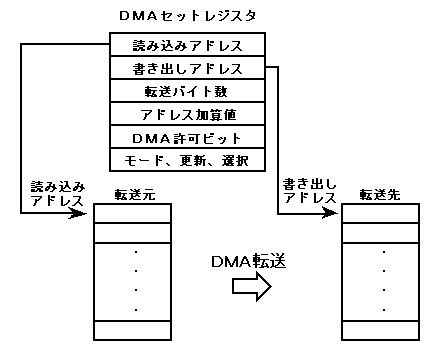
In contrast to the direct mode, the mode that indirectly uses the level-specific DMA set register to execute DMA transfer is called the indirect mode. In direct mode, the address value and the number of bytes stored in the set register are stored in the indirect mode temporary buffer in indirect mode, and the DMA transfer is repeatedly executed until the exit code in the buffer is detected. Therefore, the feature of indirect mode is that multiple DMA transfers can be executed with one startup. Figure 2.5 shows the indirect mode DMA execution flow. Figure 2.5 Indirect mode DMA transfer flow
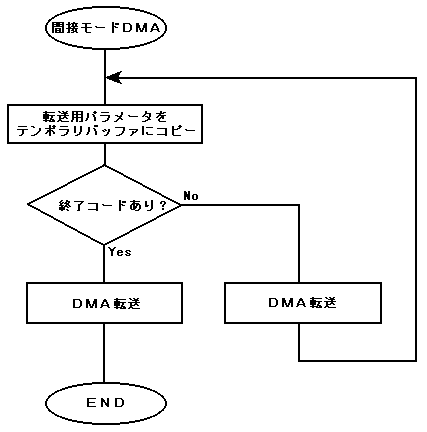
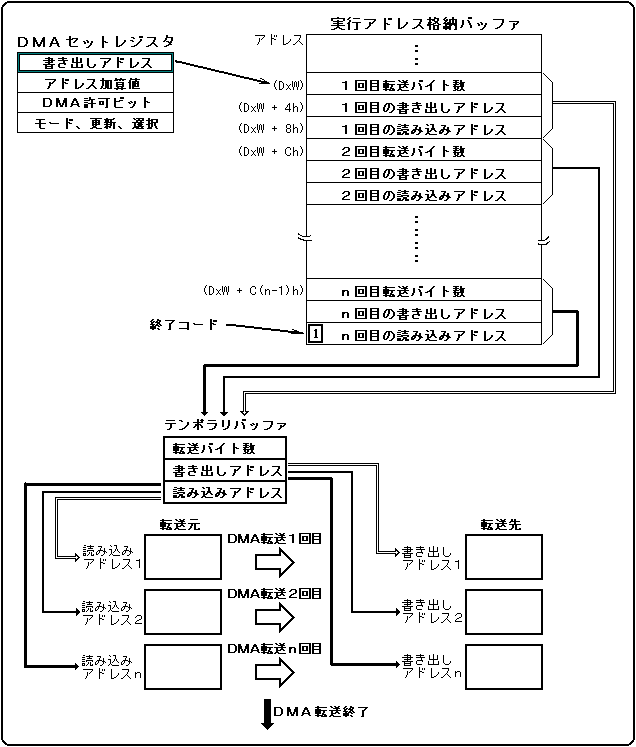
When indirect mode is activated, the parameters for 3 longwords are first read from the address written in the write address register (DxW) and stored in the temporary buffer. Then perform the actual DMA based on that parameter. After the DMA is completed, read the address ~ parameter of DxW + CH and execute in the same way. This operation is repeated until an exit code is detected.
Also, the address in indirect mode is incremented in 4-byte increments. Figure 2.6 Details of indirect mode DMA transfer operation


 ★ HARDWARE Manual ★ SCU User's Manual
★ HARDWARE Manual ★ SCU User's Manual