■ 2.1 DMA transfer
◆ Basic operation of DMA
Figure 2.1 shows an example of performing DMA transfer from the transfer source address 1H to 50H to the transfer destination address 6H to 55H. At the transfer source, the longword boundary is 4H, so 1H to 3H is read in byte units. increase. On the other hand, at the transfer destination, the longword boundary is 8H, so the first 2 bytes of the read data are written to 6H to 7H in byte units. Furthermore, the transfer source end address is 50H, but the longword boundary is up to 4FH, so 50H data is read in bytes. On the other hand, the transfer destination end address is 55H, but the longword boundary is up to 53H, so the last 2 bytes read are written to 54H to 55H in byte units.
Figure 2.1 Basic operation of DMA transfer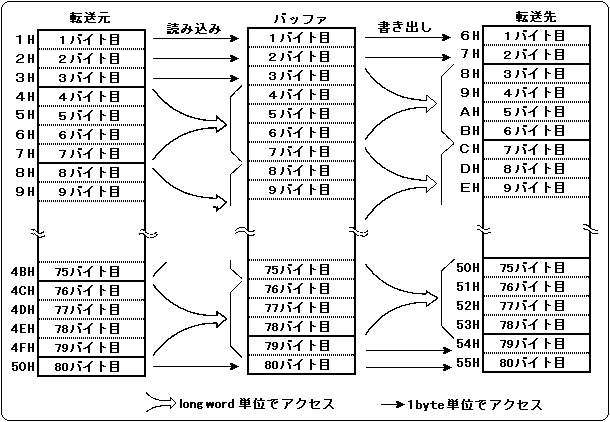
- DMA startup from main CPU
- DMA activation from DSP
Figure 2.2 DMA transferable area when booted from the main CPU
Figure 2.3 DMA transferable area when booted from DSP 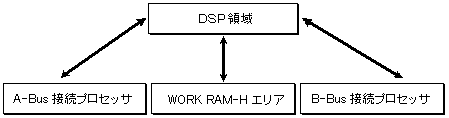
 | Precautions regarding DMA |
|---|
For example, when continuous write is executed on the CPU for VDP1 (B-Bus), continuous write ends even if SCU-DMA is started from A-Bus to VDP2 (B-Bus). SCU-DMA will not start until you do.
However, CPU access to A-Bus and B-Bus is waited for while SCU-DMA is running.
If 3 channels are used at the same time, the priority will be ignored. (DSP DMA instructions are also counted as one channel)
As a countermeasure, do not start DMA level 2 while starting with DMA level 1.
It hangs when rewritten.
Perform SCU-DMA direct mode, CPU-DMA or software transfer.
For transfers that use the A-BUS space as the source as well as the CD buffer, only "4 byte addition" can be specified for the source read address addition value , and the setting of "do not add" is prohibited.
There is no such limitation for SCU-DMA direct mode.
 ★ HARDWARE Manual ★ SCU User's Manual
★ HARDWARE Manual ★ SCU User's Manual