4.1 Library configuration
application | |
|---|---|
Stream system library | MPEG library |
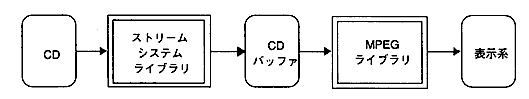
To use this library, you need to link the following libraries at the same time.
- SEGA_STM.LIB: Stream system library
- SEGA_GFS.LIB: File system library
- SEGA_CDC.LIB: CD communication interface library
- SEGA_DMA.LIB: DMA library
- SEGA_CSH.LIB: Cache library
4.2 Capture the state of the MPEG system
Therefore, call the MPG_CaptStat function at either of the following timings for each VSYNC to capture the state of the MPEG system.
- Clear the MPCM flag with a VBLANK-IN interrupt and wait for it to turn ON before calling.
- Call with VBLANK-OUT interrupt
- MPG_Init
- MPG_ResetMp
- MPG_CaptStat
- MPG_MvStart
- MPG_MvStopVideo
- MPG_MvGetVideoStat
- MPG_MvEntryNext
- MPG_MvStop
- MPG_MvStopAudio
- MPG_MvGetAudioStat
- MPG_MvChange
- MPG_SpStart
- MPG_SpGetVideoStat
- MPG_SpStop
4.3 VDP2 output mode
Since it is difficult for the application software to obtain the VSYNC timing on this game machine, it is recommended to perform MPEG-related processing from the VBLANK-OUT timing.
Figure 4.2 Timing of processing at VDP2 output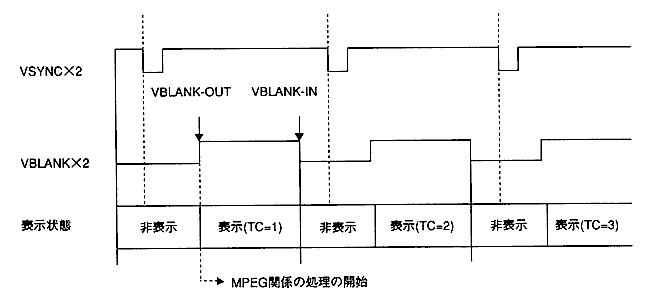
- Wait for VBLANK-OUT.
- Call the MPG_CaptStat function.
- Get the timecode.
- Get the collision data corresponding to the time code.
- Perform collision detection, etc., and make MPEG-related settings corresponding to the results.
- The setting of (5) becomes effective in the next frame.
4.4 Host transfer mode
4.5 State transition
The MPEG handle holds the video and audio operating states. The operating status transitions as follows for both video and audio.
Use the following functions to start and stop playback.
- Playback start function
- MPG_MvStart
- MPG_SpStart
- Playback stop function
- MPG_MvStop, MPG_MvStopVideo, MPG_MvStopAudio
- MPG_SpStop
Figure 4.3 State transition diagram of MPEG handle
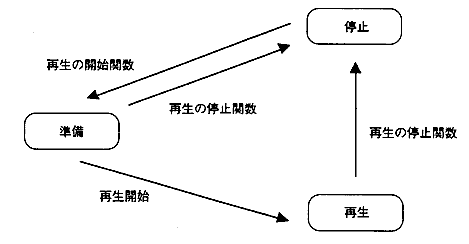
- Playback stop function behavior
- If the decoder is initialized in the play stop function, the MPEG screen display will be set to ON in the library.
- Clear the VBV buffer in the MPG_MvStop function, MPG_MvStopVideo function, and MPG_SpStop function.
- When the video playback is stopped, the next stream is canceled for the MPEG system.
4.6 Hang up detection
Hang-up detection is performed by calling the MPG_ResetHng function once and then calling the MPG_CheckHng function for each VSYNC.
If it hangs, stop MPEG playback and then start MPEG playback again. If this action does not recover, initialize it with the MPG_Init function.
4.7 User transfer function registration
The specifications of the transfer function are as follows.
[Form] Sint32 trFunc (void * dst, void * src, Sint32 nbyte) [Input] dst: Transfer destination address src: Transfer source address nbyte: Number of transfer bytes [Function value] Error code
- dst contains the address of the transfer area set by the MPG_WnSetOutputMode function.
- The transfer function is called from the MPEG library when you execute the MPG_WnTrans function.
- To register the transfer function, use the MPG_WnEntryTrFunc function.
- By default, the DMA transfer function on the B-Bus by SCU is registered in the transfer function.
- The default transfer function times out in about 2 seconds if the DMA transfer is not complete.
4.8 Precautions for use
MPG_MvSetVideoId
- Call the MPG_MvStopAudio function.
- Make sure the audio is stopped by the MPG_MvGetAudioStat function.
- Call the MPG_MvStopVideo function.
 ★ PROGRAMMER'S GUIDE ★ MPEG library
★ PROGRAMMER'S GUIDE ★ MPEG library