4-1. Model data specifications
The general format when the model name is assumed to be "label" is shown below.
Point data
POINT point_label [] = {
POStoFIXED (x, y, z),
POStoFIXED (x, y, z),
POStoFIXED (x, y, z),
POStoFIXED (x, y, z),
.............
};
POINT: Point data
x, y, z: Float type coordinate valuesPolygon data
POLYGON polygon_label [] = {
NORMAL (x, y, z),
VERTICES (0,1,2,3),
NORMAL (x, y, z),
VERTICES (0,1,2,3),
.............
};
NORMAL: normal vector
x, y, z: Float type coordinate values
VERTICES: Point data of 4 points forming a polygonAttribute data
ATTR attribute_label = [] = {
ATTRIBUTE (Plane, Sort, Texture, Color, Gouraud, Mode, Dir, Option),
....... .... ..... ... ... ..... ... .....
};
ATTR: Attribute
Plane: Attribute of whether or not there is backside judgment Sort: Representative point of Z sort
Texture: Texture name (No.)
Color: Color data
Gouraud: Gouraud shading attribute Mode: Drawing mode
Dir: Polygon and texture state Option: Options and other features
r, g, and b each represent the three primary colors and contain decimal values from 0 to 31.
| group | macro | Contents |
|---|---|---|
| [1] | No_Window | Unrestricted in Window (default) | Window_In | Display inside the Window | Window_Out | Display outside the window |
| [2] | MESHoff | Normal display (default) | MESHon | Display as a mesh |
| [3] | ECdis | Disable End Code | ECenb | Enable End Code (default) |
| [4] | SPdis | Also show transparent pixels (default) | SPenb | Do not show transparent pixels |
| [5] | CL16Bnk | 16-color color bank mode (default) | CL16Look | 16-color look-up table mode | CL64Bnk | 64 color color bank mode | CL128Bnk | 128 color color bank mode | CL256Bnk | 256 color color bank mode | CL32KRGB | 32768 color RGB mode |
| [6] | CL_Replace | Overwrite (standard) mode (default) | CL_Shadow | Shadow mode | CL_Half | Semi-brightness mode | CL_Trans | Semi-transparent mode | CL_Gouraud | Gouraud shading mode |
| macro | Contents |
|---|---|
| sprNoflip | Display textures normally |
| sprHflip | Flip the texture left and right |
| sprVflip | Flip the texture upside down |
| sprHVflip | Flip the texture up / down / left / right |
| sprPorygon | Show polygons |
| sprPolyLine | Show polyline |
| sprLine | Display a straight line using the first two points |
| macro | Contents |
|---|---|
| UseLight | Perform light source calculation |
| UseClip | Do not display when the vertices go off the screen |
| UsePalette | Indicates that the polygon color is in palette format |
PDATA structure
PDATA pdata_label [] = {
point_label, n1,
polygon_label, n2,
attribute_label
};
pdata_label: Indicates the PDATA type address to be passed to SGL.
point_label: Indicates a POINT type address.
nl: Indicates the number of points.
polygon_label: Indicates a POLYGON type address.
n2: Indicates the number of polygons.
attribute_label: Indicates an ATTR type address.
OBJECT structure
OBJECT object_label [] = {
pdata_label,
TRANSLATION (x, y, z),
ROTATION (x, y, z),
SCALING (x, y, z),
object_child,
object_sibling,
pdata_label: Indicates a PDATA type address.
TRANSLATION: Indicates the amount of movement.
ROTATION: Indicates the amount of rotation.
SCALING: Indicates the amount of enlargement.
object_child: Indicates the OBJECT type address of the child.
object_sibling: Indicates the OBJECT type address of siblings.
4-2. Material name specifications
It will be.
4-3. Texture data specifications
TEXDAT sample [] = {
rgb, rgb, rgb, rgb, rgb, rgb, rgb, rgb
rgb, rgb, rgb, rgb, rgb, rgb, rgb, rgb
.............................
};
TEXTB: Texture table
sample: Indicates a label with texture data (file name as it is)
hsize, vsize: The size of the texture (hsize is always a multiple of 8)
bgr: 1 pixel of texture data
The data format is as follows.
| B | G | R | |||||||||||||
| 1 | Four | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | Four | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | Four | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
Figure 4-1 Checkered texture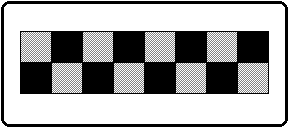
TEXDAT sample [] = {
0xffff, 0x8000, 0xffff, 0x8000, 0xffff, 0x8000, 0xffff, 0x8000,
0x8000,0xffff, 0x8000,0xffff, 0x8000,0xffff, 0x8000,0xffff
};
 ★ SGL User's Manual ★ Data transfer
★ SGL User's Manual ★ Data transfer