3-1. Light source
However, it takes an enormous amount of time to calculate all of these as light source information and draw them accurately. Therefore, in SGL, only the light source direction is selected from these light source information and reflected in the polygon drawing.
Also, regarding the direction of light, light is usually defined as radiation from a certain point, which is also too time-consuming to calculate. Therefore, assuming that the light source position is infinity, the direction of the light is treated as if it is always emitted from the same direction regardless of the coordinate position of the object.
<Fig. 3-1 Light source image model>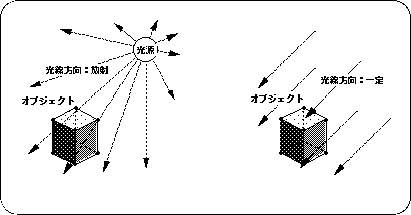
Light source changes on the surface of an object are determined by the direction of the rays and the orientation of the normal vector on each polygonal surface. The image below shows this image.
Figure 3-2 Shadow image model Shadow of polygonal surface by light source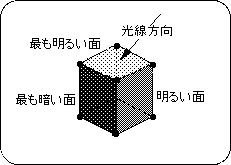
3-2. Light source setting
[Void slLight (VECTOR light);]
Substitute a VECTOR type variable (light source vector) that indicates the direction of the ray as a parameter.
Information such as light source intensity and color information is not included in the parameters.
In SGL, a ray is defined as always shining from the direction of the specified direction vector.
Also, unless you turn on light source calculation in the surface attributes of the object, setting the light source does not reflect the shadows caused by the light source (see “ Chapter 7 Polygon Surface Attributes ” for details).
The polygon surface determines the polygon color from the angle of incidence of light on the surface.
The closer the angle of incidence is to vertical, the brighter it is, and the closer it is to horizontal, the darker it is. Also, the negative vertical direction is the darkest.
Precautions when setting the light source
This happens because the user uses a matrix operation to calculate the light source vector specified by the function “ slLight”. Therefore, when setting the light source, it is necessary to initialize the current matrix.
Use the function “ slPushUnitMatrix ” or “ slUnitMatrix ” to initialize the current matrix.
[Bool slPushUnitMatrix (void)]
The previous current matrix is temporarily stored at a higher level in the stack.
[Void slUnitMatrix (MATRIX mtptr)]
Assign the specified MATRIX type variable to the parameter.
If "CURRENT" is specified for the parameter, the conversion target matrix will be the current matrix, and the current matrix can be initialized.
For details on the current matrix and matrix functions, refer to " Chapter 5 Matrix".
Listing 3-1 below shows the changes in the shadows on the cube polygon plane when the direction vector of the light source is changed one after another for a cube placed in space.
/ * ------------------------------------------------ ---------------------- * /
/ * Cube & A Light Source * /
/ * ------------------------------------------------ ---------------------- * /
#include "sgl.h"
extern PDATA PD_PLANE1;
void ss_main (void)
{
static ANGLE ang [XYZ];
static FIXED pos [XYZ];
static FIXED light [XYZ];
static ANGLE tmp = DEGtoANG (0.0);
slInitSystem (TV_320x224, NULL, 1);
ang [X] = DEGtoANG (30.0);
ang [Y] = DEGtoANG (45.0);
ang [Z] = DEGtoANG (0.0);
pos [X] = toFIXED (0.0);
pos [Y] = toFIXED (0.0);
pos [Z] = toFIXED (190.0);
light [X] = toFIXED (-1.0);
light [Y] = toFIXED (0.0);
light [Z] = toFIXED (0.0);
slPrint ("Sample program 3.2", slLocate (9,2));
while (-1) {
slPushMatrix ();
{
slRotY (tmp);
slRotX (DEGtoANG (15.0));
slRotZ (DEGtoANG (15.0));
slCalcPoint (toFIXED (0.0), toFIXED (0.0), toFIXED (1.0), light);
}
slPopMatrix ();
slLight (light);
tmp + = DEGtoANG (1.0);
slPushMatrix ();
{
slTranslate (pos [X], pos [Y], pos [Z]);
slRotX (ang [X]);
slRotY (ang [Y]);
slRotZ (ang [Z]);
slPutPolygon (& PD_PLANE1);
}
slPopMatrix ();
slSynch ();
}
}
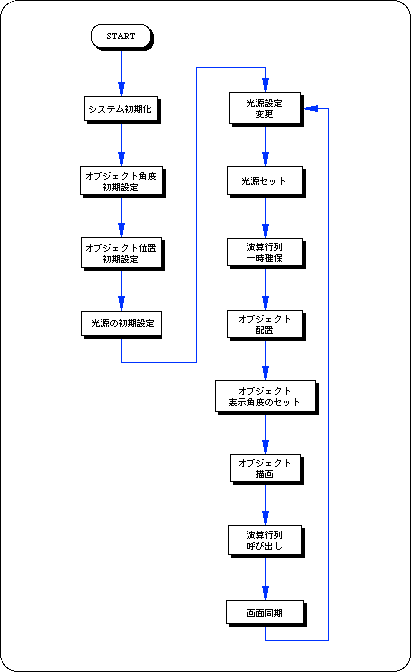
Flow 3-1 sample_3_2: Light source movement flowchart
Appendix SGL library functions that appeared in this chapter
| Functional type | Function name | Parameters | function |
|---|---|---|---|
| void | slLight | VECTOR light | Light source vector settings |
| Bool | slPushUintMatrix | void | Secure the identity matrix on the stack |
| void | slUintMatrix | MATRIX mptrt | Make the specified matrix an identity matrix |
 ★ SGL User's Manual ★ PROGRAMMER'S STRUCT
★ SGL User's Manual ★ PROGRAMMER'S STRUCT